Reverse Vaccinology Approach in Constructing a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Against Cancer-Testis Antigens Expressed in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 34048178
- PMCID: PMC8408400
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.5.1495
Reverse Vaccinology Approach in Constructing a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Against Cancer-Testis Antigens Expressed in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Background: The 5-year survival rate of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients has not significantly improved despite advancements in the currently applied treatments. Thus, efforts are put forth in developing novel immunotherapeutic agents targeting cancer-testis antigens (CTA) in NSCLC. This work utilized reverse vaccinology approach in designing a novel multi-epitope vaccine targeting melanoma-associated antigen 3 (MAGEA3), MAGEA4, New York esophageal squamous cell carcinoma-1 (NY-ESO-1), and Kita-Kyushu lung cancer antigen 1 (KK-LC1), being the most frequently expressed CTAs in NSCLC.
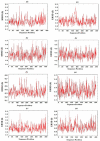
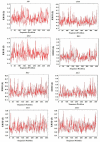
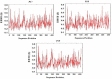
Methods: Epitopes were mapped from the sequences of CTAs. The population coverage (PC) of identified CD4+ and CD8+ epitopes were estimated. Candidate linear B cell (BL), CD4+, and CD8+ epitopes were adjoined in a multi-epitope construct (Mvax) with flagellin domain as an adjuvant. Antigenicity, and cross-reactivity of Mvax were examined. The tertiary structure of Mvax was modelled, and validated. All epitopes included in the vaccine were docked with their human leukocyte antigen (HLA) binders. The immunogenicity of epitopes in Mvax was validated through molecular dynamics analysis.
Results: Mvax contains 22 epitopes from MAGEA3, MAGEA4, NY-ESO-1, and KK-LC1. It is classified as antigenic, non-allergen, non-toxic, and possesses physicochemical stability. Epitopes have no significant hits with other human proteins, except for 2 other CTAs frequently expressed in NSCLC. The stretch of BL epitopes in Mvax confers flexibility, and accessibility emphasizing its antigenicity. The tertiary structure analysis showed that Mvax model has good structural quality. All epitopes included in the vaccine are highly immunogenic as indicated by favorable binding affinity, low binding energy, and acceptable root-mean-square deviation (RMSD). CD4+ and CD8+ epitopes have global PC of 81.81%, and 84.15%, respectively.
Conclusion: Overall, in silico evaluations show that Mvax is a potential immunotherapeutic agent against NSCLC.
Keywords: In Silico; Keywords: NSCLC; cancer-testis antigen; reverse vaccinology.
Conflict of interest statement
Author has no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In Silico Approach in Designing a Novel Multi-Epitope Vaccine Candidate against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Overexpressed G Protein-Coupled Receptor 56.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 Aug 1;21(8):2297-2306. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.8.2297. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32856858 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive and prognostic effect of CD133 and cancer-testis antigens in stage Ib-IIIA non-small cell lung cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):5509-18. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191258 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of cancer-testis antigens MAGE-A3/6 and NY-ESO-1 in non-small-cell lung carcinomas and their relationship with immune cell infiltration.Lung. 2009 Nov-Dec;187(6):401-11. doi: 10.1007/s00408-009-9181-3. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Lung. 2009. PMID: 19795170
-
NY-ESO-1 Based Immunotherapy of Cancer: Current Perspectives.Front Immunol. 2018 May 1;9:947. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00947. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29770138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune modulations during chemoimmunotherapy & novel vaccine strategies--in metastatic melanoma and non small-cell lung cancer.Dan Med J. 2013 Dec;60(12):B4774. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 24355457 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the role and mechanisms of MAGEA4 in tumorigenesis, regulation, and immunotherapy.Mol Med. 2025 Feb 4;31(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01079-8. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39905312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer-testis antigen KK-LC-1 is a potential biomarker associated with immune cell infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jul 30;22(1):834. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09930-5. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35907786 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and Exploration of Small Molecule Binders for CT83: Computational Insights from Homology Modeling, Virtual Screening, MD Simulations, Interaction Fingerprint, and Network Communications.ACS Omega. 2025 May 23;10(22):22884-22908. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00053. eCollection 2025 Jun 10. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40521510 Free PMC article.
-
The Promising Potential of Reverse Vaccinology-Based Next-Generation Vaccine Development over Conventional Vaccines against Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jul 20;11(7):1264. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11071264. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37515079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening of Oncogenic Proteins and Development of a Multiepitope Peptide Vaccine Targeting AKT1 and PARP1 for Breast Cancer by Integrating Reverse Vaccinology and Immune-Informatics Approaches.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025 Jan 1;26(1):327-338. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2025.26.1.327. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025. PMID: 39874016 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

