Rosmarinic Acid Induces Proliferation Suppression of Hepatoma Cells Associated with NF-κB Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 34048194
- PMCID: PMC8408391
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.5.1623
Rosmarinic Acid Induces Proliferation Suppression of Hepatoma Cells Associated with NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Background: Rosmarinic acid (RA) is a natural phenolic compound that acts as a Fyn inhibitor by 53 homology modeling of the human Fyn structure. Therefore, the apoptosis mechanism related to NF-κB signaling pathway induced by RA in HepG2 was investigated.
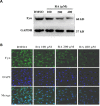
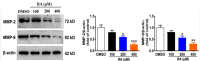
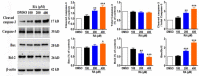
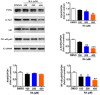
Methods: The cell growth, apoptosis, and proliferation of HepG2 regulated by various concentrations of RA were studied. The proteins expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, PI3K, AKT, NF-κB, and apoptosis-related proteins Bax, Bcl-2, cleaved caspase-3 were detected.
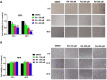
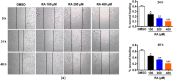
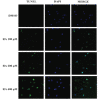
Results: RA significantly reduced proliferation rates, inhibited migration and invasion, and decreased the expressions of invasion-related factors, such as matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9. TUNEL staining revealed that RA resulted in a dose-dependent increase of HepG2 cell apoptosis. In line with this finding, the expression of apoptosis suppressor protein Bcl-2 was downregulated and that of the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and cleaved caspase-3 was increased. In addition, we found that the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway was involved in RA-mediated inhibition of HepG2 cell metastasis.
Conclusion: Our study identified that RA as a drug candidate for the treatment of HCC.
Keywords: HepG2 cells; Proliferation; Rosmarinic acid (RA); hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declares that we have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alcaraz M, Alcaraz-Saura M, Achel DG, et al. Radiosensitizing effect of rosmarinic acid in metastatic melanoma B16F10 cells. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:1913–21. - PubMed
-
- Bosetti C, Turati F, La Vecchia C. Hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2014;28:753–70. - PubMed
-
- Cheng JC, Chou CH, Kuo ML, Hsieh CY. Radiation-enhanced hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion with MMP-9 expression through PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. Oncogene. 2006;25:7009–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

