An incoherent feedforward loop formed by SirA/BarA, HilE and HilD is involved in controlling the growth cost of virulence factor expression by Salmonella Typhimurium
- PMID: 34048498
- PMCID: PMC8192010
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009630
An incoherent feedforward loop formed by SirA/BarA, HilE and HilD is involved in controlling the growth cost of virulence factor expression by Salmonella Typhimurium
Abstract
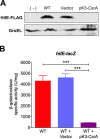
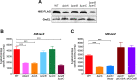
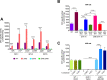
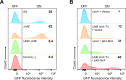
An intricate regulatory network controls the expression of Salmonella virulence genes. The transcriptional regulator HilD plays a central role in this network by controlling the expression of tens of genes mainly required for intestinal colonization. Accordingly, the expression/activity of HilD is highly regulated by multiple factors, such as the SirA/BarA two-component system and the Hcp-like protein HilE. SirA/BarA positively regulates translation of hilD mRNA through a regulatory cascade involving the small RNAs CsrB and CsrC, and the RNA-binding protein CsrA, whereas HilE inhibits HilD activity by protein-protein interaction. In this study, we show that SirA/BarA also positively regulates translation of hilE mRNA through the same mentioned regulatory cascade. Thus, our results reveal a paradoxical regulation exerted by SirA/BarA-Csr on HilD, which involves simultaneous opposite effects, direct positive control and indirect negative control through HilE. This kind of regulation is called an incoherent type-1 feedforward loop (I1-FFL), which is a motif present in certain regulatory networks and represents a complex biological problem to decipher. Interestingly, our results, together with those from a previous study, indicate that HilE, the repressor component of the I1-FFL reported here (I1-FFLSirA/BarA-HilE-HilD), is required to reduce the growth cost imposed by the expression of the genes regulated by HilD. Moreover, we and others found that HilE is necessary for successful intestinal colonization by Salmonella. Thus, these findings support that I1-FFLSirA/BarA-HilE-HilD cooperates to control the precise amount and activity of HilD, for an appropriate balance between the growth cost and the virulence benefit generated by the expression of the genes induced by this regulator. I1-FFLSirA/BarA-HilE-HilD represents a complex regulatory I1-FFL that involves multiple regulators acting at distinct levels of gene expression, as well as showing different connections to the rest of the regulatory network governing Salmonella virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proteomic analysis reveals the global effect of the BarA/SirA-Csr regulatory cascade in Salmonella Typhimurium grown in conditions that favor the expression of invasion genes.J Proteomics. 2023 Aug 30;286:104960. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2023.104960. Epub 2023 Jul 13. J Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 37451358
-
Integration of a complex regulatory cascade involving the SirA/BarA and Csr global regulatory systems that controls expression of the Salmonella SPI-1 and SPI-2 virulence regulons through HilD.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Jun;80(6):1637-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07674.x. Epub 2011 May 12. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21518393 Free PMC article.
-
HilE Regulates HilD by Blocking DNA Binding in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2018 Mar 26;200(8):e00750-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00750-17. Print 2018 Apr 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29378886 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella invasion gene regulation: a story of environmental awareness.J Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43 Spec No:110-7. J Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15765064 Review.
-
Genetic and environmental control of salmonella invasion.J Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43 Spec No:85-92. J Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15765061 Review.
Cited by
-
Incoherent merger network for robust ratiometric gene expression response.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Apr 11;51(6):2963-2973. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad087. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36840726 Free PMC article.
-
A trans-acting sRNA SaaS targeting hilD, cheA and csgA to inhibit biofilm formation of S. Enteritidis.J Adv Res. 2025 May;71:127-139. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.06.008. Epub 2024 Jun 7. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38852803 Free PMC article.
-
CsrA Positively and Directly Regulates the Expression of the pdu, pocR, and eut Genes Required for the Luminal Replication of Salmonella Typhimurium.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0151623. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01516-23. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37358421 Free PMC article.
-
The Two-Component System CpxRA Represses Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 2 by Directly Acting on the ssrAB Regulatory Operon.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0271022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02710-22. Epub 2022 Sep 8. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36073960 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Evolution of the phoH Ancestral Gene in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2022 May 17;204(5):e0058521. doi: 10.1128/jb.00585-21. Epub 2022 Apr 11. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 35404111 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

