Successful containment of a flight-imported COVID-19 outbreak through extensive contact tracing, systematic testing and mandatory quarantine: Lessons from Vietnam
- PMID: 34048935
- PMCID: PMC8149171
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2021.102084
Successful containment of a flight-imported COVID-19 outbreak through extensive contact tracing, systematic testing and mandatory quarantine: Lessons from Vietnam
Abstract
Background: The importation of SARS-CoV-2 through air travel poses substantial risks to generate new COVID-19 outbreaks. Timely contact tracing is particularly crucial to limit onwards transmission in settings without established community transmission.
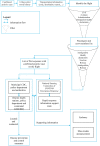
Methods: We conducted an in-depth analysis of the response to a big flight-associated COVID-19 outbreak in Vietnam in March 2020 that involved contact tracing, systematic testing and strict quarantine up to third generation contacts.
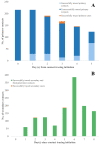
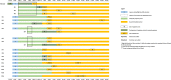
Results: 183 primary contacts from the flight as well as 1000 secondary and 311 third generation contacts were traced, tested, and quarantined across 15 provinces across Vietnam. The protracted confirmation of the index case at 3 days and 19 h after arrival resulted in isolation/quarantine delays of 6.8 days (IQR 6.3-6.8) and 5.8 days (IQR 5.8-7.0) for primary and secondary cases, respectively, which generated 84.0 and 26.4 person-days of community exposure from primary and secondary cases, respectively. Nevertheless, only 5 secondary cases occurred.
Conclusions: A large flight-related COVID-19 cluster was successfully contained through timely, systematic and comprehensive public health responses despite delayed index case identification. Multiagency collaboration and pre-established mechanisms are crucial for low and middle income countries like Vietnam to limit community transmission after COVID-19 importation through air travel.
Keywords: Air travel; COVID-19; Case importation; Cluster containment; Contact tracing; Vietnam.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Khanh N.C., Thai P.Q., Quach H.-L., Thi N.-A.H., Dinh P.C., Duong T.N., et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV 2 during long-haul flight. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 Nov;26(11) https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/26/11/20-3299_article [Internet] 2617–24. Available from. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Freedman D.O., Wilder-Smith A. In-flight transmission of SARS-CoV-2: a review of the attack rates and available data on the efficacy of face masks. J Trav Med. 2020 Sep 25;2020:1–7. https://academic.oup.com/jtm/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jtm/taaa178/591... [Internet] Available from. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vietnam Ministry of Health . Vietnam Ministry of Health Portal; 2020. Decision No. 343/QĐ-BYT date February 7 2020 on “Official guidelines for surveillance, prevention and control measures for acute pneumonia infecition caused by novel corona virus nCoV”.https://moh.gov.vn/web/dich-benh/huong-dan-chuyen-mon/-/asset_publisher/... [Internet] Available from.
-
- General Department of Preventive Medicine VM of H . Digital Communication Department, General Department of Preventive Medicine; 2020. Lists of Eligible laboratory departments for COVID-19 testing and confirmation.http://vncdc.gov.vn/vi/phong-chong-dich-benh-viem-phoi-cap-ncov/11871/ca... [Internet] Available from.
-
- Official Page for acute respiratory disease COVID-19 . Vietnam Ministry of Health; 2020. Compulsory mask wearing measures in Vietnam: q&A.https://ncov.moh.gov.vn/en/-/khi-bat-buoc-eo-khau-trang-noi-cong-cong-un... [Internet] Available from.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

