Nanoparticles for co-delivery of osimertinib and selumetinib to overcome osimertinib-acquired resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 34048974
- PMCID: PMC8273131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.05.018
Nanoparticles for co-delivery of osimertinib and selumetinib to overcome osimertinib-acquired resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
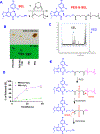
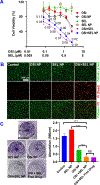
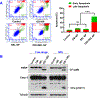
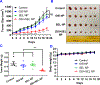
Osimertinib (OSI) is the first FDA-approved third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). It can be used for treating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with activating EGFR mutation and for patients who are resistant to first-generation EGFR TKIs due to T790M resistance mutation. However, patients treated with OSI ultimately develop acquired resistance, which prevents its long-term benefit for patients. Therefore, the development of effective strategies to overcome OSI resistance will address a significant clinical challenge and benefit patients by prolonging their survival time. Our previous studies indicated that combination therapy was a promising strategy for overcoming OSI resistance. In this study, we developed nanoparticle (NP) formulations for co-delivery of osimertinib (OSI) and selumetinib (SEL) to treat OSI-resistant NSCLC effectively. We conjugated SEL with PEG through a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive linker to generate polyethylene glycol (PEG)-SEL conjugate prodrug (PEG-S-SEL). Due to the amphiphilic nature of PEG-S-SEL, it can self-assemble in an aqueous solution to form micelle NP and serve as a delivery carrier for OSI. The ROS-responsive linker can facilitate the release of drugs in the tumor microenvironment with elevated ROS levels. OSI and SEL combination NP can overcome OSI resistance by simultaneously inhibiting both EGFR and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK), thus effectively inducing apoptosis in OSI-resistant NSCLC cells and inhibiting OSI-resistant tumors in vivo. In conclusion, the OSI+SEL NP combination therapy showed promising anticancer efficacy and demonstrated potential for treating NSCLC patients with OSI acquired resistance. STATEMENT OF SIGNIFICANCE: Osimertinib (OSI) is the first FDA-approved third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor. It has been successfully used for treating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with activating EGFR mutation. However, patients treated with OSI ultimately develop acquired resistance. This study developed OSI and selumetinib (SEL) co-delivering nanoparticles to overcome OSI-acquired resistance in NSCLC. PEG-SEL conjugate functions as reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive prodrug and forms micelle nanoparticles through self-assembly to deliver OSI. The combination NP can simultaneously inhibit EGFR and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK), thus effectively inducing apoptosis in OSI-resistant NSCLC cells. In summary, the OSI and SEL nanoparticle combination therapy showed promising anticancer efficacy and demonstrated potential for treating NSCLC patients with OSI acquired resistance.
Keywords: Acquired resistance; Non-small Cell Lung Cancer; Osimertinib; Prodrug; Reactive Oxygen Species; Selumetinib.
Copyright © 2021 Acta Materialia Inc. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A, Cancer statistics, 2018, CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 68 (2018) 7–30. - PubMed
-
- Lim SM, Syn NL, Cho BC, Soo RA, Acquired resistance to EGFR targeted therapy in non-small cell lung cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies, Cancer Treat Rev 65 (2018) 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Cross DA, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S, Eberlein C, Nebhan CA, Spitzler PJ, Orme JP, Finlay MR, Ward RA, Mellor MJ, Hughes G, Rahi A, Jacobs VN, Red Brewer M, Ichihara E, Sun J, Jin H, Ballard P, Al-Kadhimi K, Rowlinson R, Klinowska T, Richmond GH, Cantarini M, Kim DW, Ranson MR, Pao W, AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer, Cancer Discov 4 (2014) 1046–61. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard D, Cho BC, Gray JE, Ohe Y, Zhou C, Reungwetwattana T, Cheng Y, Chewaskulyong B, Shah R, Cobo M, Lee KH, Cheema P, Tiseo M, John T, Lin MC, Imamura F, Kurata T, Todd A, Hodge R, Saggese M, Rukazenkov Y, Soria JC, Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC, N Engl J Med 382 (2020) 41–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

