Human pluripotent stem cell-derived brain organoids as in vitro models for studying neural disorders and cancer
- PMID: 34049587
- PMCID: PMC8161602
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-021-00617-1
Human pluripotent stem cell-derived brain organoids as in vitro models for studying neural disorders and cancer
Abstract
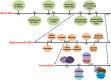
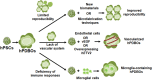
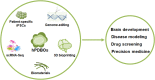
The sheer complexities of brain and resource limitation of human brain tissue greatly hamper our understanding of the brain disorders and cancers. Recently developed three-dimensional (3D) brain organoids (BOs) are self-organized and spontaneously differentiated from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) in vitro, which exhibit similar features with cell type diversity, structural organization, and functional connectivity as the developing human brain. Based on these characteristics, hPSC-derived BOs (hPDBOs) provide new opportunities to recapitulate the complicated processes during brain development, neurodegenerative disorders, and brain cancers in vitro. In this review, we will provide an overview of existing BO models and summarize the applications of this technology in modeling the neural disorders and cancers. Furthermore, we will discuss the challenges associated with their use as in vitro models for disease modeling and the potential future direction.
Keywords: Brain organoids; Cancer; Human pluripotent stem cells; Neural disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human pluripotent stem cell-derived lung organoids: Potential applications in development and disease modeling.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2021 Nov;10(6):e399. doi: 10.1002/wdev.399. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33145915 Review.
-
Modeling and Targeting Alzheimer's Disease With Organoids.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 31;11:396. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00396. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32300301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patterning of brain organoids derived from human pluripotent stem cells.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2022 Jun;74:102536. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2022.102536. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35405627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modelling neurodegenerative diseases with 3D brain organoids.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2020 Oct;95(5):1497-1509. doi: 10.1111/brv.12626. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2020. PMID: 32568450 Review.
-
Challenges in Modeling Human Neural Circuit Formation via Brain Organoid Technology.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Dec 3;14:607399. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.607399. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33362473 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Brain tumors and induced pluripotent stem cell technology: a systematic review of the literature.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 Jan 9;87(1):250-264. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002760. eCollection 2025 Jan. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40109603 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress in Flexible Microelectrode Arrays for Combined Electrophysiological and Electrochemical Sensing.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Feb 10;15(2):100. doi: 10.3390/bios15020100. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39997002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling Human Brain Tumors and the Microenvironment Using Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 16;15(4):1253. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041253. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Building on a Solid Foundation: Adding Relevance and Reproducibility to Neurological Modeling Using Human Pluripotent Stem Cells.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Nov 18;15:767457. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.767457. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34867204 Free PMC article.
-
Human mini brains and spinal cords in a dish: Modeling strategies, current challenges, and prospective advances.J Tissue Eng. 2022 Jul 21;13:20417314221113391. doi: 10.1177/20417314221113391. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. J Tissue Eng. 2022. PMID: 35898331 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

