Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Presentation and Outcome of Consecutive Patients Admitted to Hospital Due to ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 34049671
- PMCID: PMC8075839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2021.04.011
Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Presentation and Outcome of Consecutive Patients Admitted to Hospital Due to ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
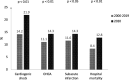
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic and pandemic-related social restrictions on clinical course of patients treated for acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is unclear. In the present study presentation and outcome of patients with STEMI in the year 2020 were compared with the years before in a German registry that includes all patients hospitalized for acute STEMI in a region with approximately 1 million inhabitants. In the year 2020 726 patients with STEMI were registered compared with 10.226 patients in the years 2006 to 2019 (730 ± 57 patients per year). No significant differences were observed between the groups regarding age, gender and medical history of patients. However, in the year 2020 a significantly higher rate of patients admitted with cardiogenic shock (21.9% vs 14.2%, p <0.01) and out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) (14.3% vs 11.1%, p <0.01) was observed. The rate of patients with subacute myocardial infarction (14.3% vs 11.6%, p <0.05) was elevated in 2020. Hospital mortality increased by 52% from the years 2006 to 2019 (8.4%) to the year 2020 (12.8%, p <0.01). Only 4 patients (0.6%) with STEMI in the year 2020 had SARS-CoV-2 infection, none of those died in-hospital. In conclusion, in the year 2020 a highly significant increase of STEMI-patients admitted to hospital with advanced infarction and poor prognosis was observed. As the structure of the emergency network to treat patients with STEMI was unchanged during the study period, the most obvious reason for these changes was COVID-19 pandemic-related lockdown and the fear of many people to contact medical staff during the pandemic.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497–506. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, Si HR, Zhu Y, Li B, Huang CL, Chen HD, Chen J, Luo Y, Guo H, Jiang RD, Liu MQ, Chen Y, Shen XR, Wang X, Zheng XS, Zhao K, Chen QJ, Deng F, Liu LL, Yan B, Zhan FX, Wang YY, Xiao GF, Shi ZL. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579:270–273. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2021. WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard.https://www.who.int (Accessed 30. March 2021)
-
- Solomon MD, McNulty EJ, Rana JS, Leong TK, Lee C, Sung SH, Ambrosy AP, Sidney S, Go AS. The Covid-19 pandemic and the incidence of acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:691–693. - PubMed
-
- De Filippo O, D'Ascenzo F, Angelini F, Bocchino PP, Conrotto F, Saglietto A, Secco GG, Campo G, Gallone G, Verardi R, Gaido L, Iannaccone M, Galvani M, Ugo F, Barbero U, Infantino V, Olivotti L, Mennuni M, Gili S, Infusino F, Vercellino M, Zucchetti O, Casella G, Giammaria M, Boccuzzi G, Tolomeo P, Doronzo B, Senatore G, Grosso Marra W, Rognoni A, Trabattoni D, Franchin L, Borin A, Bruno F, Galluzzo A, Gambino A, Nicolino A, Truffa Giachet A, Sardella G, Fedele F, Monticone S, Montefusco A, Omede P, Pennone M, Patti G, Mancone M, De Ferrari GM. Reduced rate of hospital admissions for ACS during Covid-19 outbreak in Northern Italy. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:88–89. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous