Apolipoprotein E Promotes Immune Suppression in Pancreatic Cancer through NF-κB-Mediated Production of CXCL1
- PMID: 34049975
- PMCID: PMC8445065
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3929
Apolipoprotein E Promotes Immune Suppression in Pancreatic Cancer through NF-κB-Mediated Production of CXCL1
Abstract
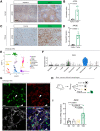
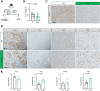
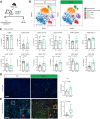
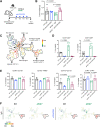
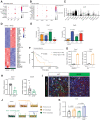
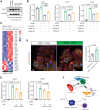
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a lethal malignancy with few effective therapeutic options. PDAC is characterized by an extensive fibroinflammatory stroma that includes abundant infiltrating immune cells. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) are prevalent within the stroma and are key drivers of immunosuppression. TAMs in human and murine PDAC are characterized by elevated expression of apolipoprotein E (ApoE), an apolipoprotein that mediates cholesterol metabolism and has known roles in cardiovascular and Alzheimer's disease but no known role in PDAC. We report here that ApoE is also elevated in peripheral blood monocytes in PDAC patients, and plasma ApoE protein levels stratify patient survival. Orthotopic implantation of mouse PDAC cells into syngeneic wild-type or in ApoE-/- mice showed reduced tumor growth in ApoE-/- mice. Histologic and mass cytometric (CyTOF) analysis of these tumors showed an increase in CD8+ T cells in tumors in ApoE-/- mice. Mechanistically, ApoE induced pancreatic tumor cell expression of Cxcl1 and Cxcl5, known immunosuppressive factors, through LDL receptor and NF-κB signaling. Taken together, this study reveals a novel immunosuppressive role of ApoE in the PDAC microenvironment. SIGNIFICANCE: This study shows that elevated apolipoprotein E in PDAC mediates immune suppression and high serum apolipoprotein E levels correlate with poor patient survival.See related commentary by Sherman, p. 4186.
©2021 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

Comment in
-
Lipid Carriers in Cancer: Context Matters.Cancer Res. 2021 Aug 15;81(16):4186-4187. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-1930. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34400469
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Crawford HC, Pasca di Magliano M. Epithelial-stromal interactions in pancreatic cancer. Annu Rev Physiol 2019;81:211–33. - PubMed
-
- Clark CE, Hingorani SR, Mick R, Combs C, Tuveson DA, Vonderheide RH. Dynamics of the immune reaction to pancreatic cancer from inception to invasion. Cancer Res 2007;67:9518–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA198074/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM145304/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM113900/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA151588/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA248160/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA214955/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007315/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM086262/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009676/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034933/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA224145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA247076/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK094775/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R50 CA232985/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA237421/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

