68Ga-Pentixafor PET/CT for Detection of Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 Expression in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
- PMID: 34049979
- PMCID: PMC8717205
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.121.262206
68Ga-Pentixafor PET/CT for Detection of Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 Expression in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
Abstract
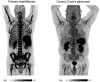
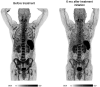
C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) is an attractive target for cancer diagnosis and treatment, as it is overexpressed in many solid and hematologic malignancies. This study investigated the feasibility of CXCR4-directed imaging with PET/CT using 68Ga-pentixafor to visualize and quantify disease involvement in myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs). Methods: Twelve patients with MPNs (4 with primary myelofibrosis, 6 with essential thrombocythemia, and 2 with polycythemia vera) and 5 controls underwent 68Ga-pentixafor PET/CT. Imaging findings were compared with immunohistochemical stainings, laboratory data, and splenic volume. Results:68Ga-pentixafor PET/CT was visually positive in 12 of 12 patients, and CXCR4 target specificity could be confirmed by immunohistochemical staining. A significantly higher tracer uptake could be detected in the bone marrow of MPN patients (SUVmean, 6.45 ± 2.34 vs. 4.44 ± 1.24). Dynamic changes in CXCR4 expression determined by 68Ga-pentixafor PET/CT corresponded with treatment response. Conclusion:68Ga-pentixafor PET/CT represents a novel diagnostic tool to noninvasively detect and quantify the extent of disease involvement in MPNs.
Keywords: CXCR4; PET; molecular imaging; myeloproliferative neoplasms; theranostics.
© 2022 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advances in PET Imaging of the CXCR4 Receptor: [68Ga]Ga-PentixaFor.Semin Nucl Med. 2024 Jan;54(1):163-170. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2023.09.002. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Semin Nucl Med. 2024. PMID: 37923671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunohistochemical detection of chemokine receptor 4 expression in chronic osteomyelitis confirms specific uptake in 68Ga-Pentixafor-PET/CT.Nuklearmedizin. 2018 Sep;57(5):198-203. doi: 10.3413/Nukmed-0971-18-04. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Nuklearmedizin. 2018. PMID: 30267402
-
(68)Ga-Pentixafor-PET/CT for Imaging of Chemokine Receptor 4 Expression in Glioblastoma.Theranostics. 2016 Jan 25;6(3):428-34. doi: 10.7150/thno.13986. eCollection 2016. Theranostics. 2016. PMID: 26909116 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging Inflammation in Atherosclerosis with CXCR4-Directed 68Ga-Pentixafor PET/CT: Correlation with 18F-FDG PET/CT.J Nucl Med. 2020 May;61(5):751-756. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.119.234484. Epub 2019 Oct 25. J Nucl Med. 2020. PMID: 31653710
-
Nuclear Medicine Application of Pentixafor/Pentixather Targeting CXCR4 for Imaging and Therapy in Related Disease.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023;23(7):787-803. doi: 10.2174/1389557523666221216095821. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36529918 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Peptides in Diagnostics.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 17;22(16):8828. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168828. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CXCR4-directed PET with 68Ga-pentixafor versus adrenal vein sampling for the diagnosis of unilateral primary aldosteronism.Endocrine. 2025 Aug;89(2):603-613. doi: 10.1007/s12020-025-04236-5. Epub 2025 May 19. Endocrine. 2025. PMID: 40388084 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR4 as a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia.Leukemia. 2024 Nov;38(11):2303-2317. doi: 10.1038/s41375-024-02326-3. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Leukemia. 2024. PMID: 39261603 Review.
-
Advances in PET Imaging of the CXCR4 Receptor: [68Ga]Ga-PentixaFor.Semin Nucl Med. 2024 Jan;54(1):163-170. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2023.09.002. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Semin Nucl Med. 2024. PMID: 37923671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
68Ga-PENTIXAFOR PET/CT Captures Superscan in Refractory Multiple Myeloma.Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther. 2025 Jun 3;34(2):162-164. doi: 10.4274/mirt.galenos.2025.94557. Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther. 2025. PMID: 40459226 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
