CBFβ promotes colorectal cancer progression through transcriptionally activating OPN, FAM129A, and UPP1 in a RUNX2-dependent manner
- PMID: 34050318
- PMCID: PMC8563980
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-021-00810-2
CBFβ promotes colorectal cancer progression through transcriptionally activating OPN, FAM129A, and UPP1 in a RUNX2-dependent manner
Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is commonly associated with aberrant transcription regulation, but characteristics of the dysregulated transcription factors in CRC pathogenesis remain to be elucidated. In the present study, core-binding factor β (CBFβ) is found to be significantly upregulated in human CRC tissues and correlates with poor survival rate of CRC patients. Mechanistically, CBFβ is found to promote CRC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and inhibit cell apoptosis in a RUNX2-dependent way. Transcriptome studies reveal that CBFβ and RUNX2 form a transcriptional complex that activates gene expression of OPN, FAM129A, and UPP1. Furthermore, CBFβ significantly promotes CRC tumor growth and live metastasis in a mouse xenograft model and a mouse liver metastasis model. In addition, tumor-suppressive miR-143/145 are found to inhibit CBFβ expression by specifically targeting its 3'-UTR region. Consistently, an inverse correlation between miR-143/miR-145 and CBFβ expression levels is present in CRC patients. Taken together, this study uncovers a novel regulatory role of CBFβ-RUNX2 complex in the transcriptional activation of OPN, FAM129A, and UPP1 during CRC development, and may provide important insights into CRC pathogenesis.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to ADMC Associazione Differenziamento e Morte Cellulare.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


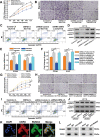
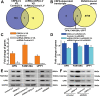
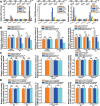


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31870821/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 31571458/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 31900458/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81972267/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 31771550/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

