Proteomic profiling for detection of early-stage heart failure in the community
- PMID: 34050710
- PMCID: PMC8318505
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.13375
Proteomic profiling for detection of early-stage heart failure in the community
Abstract
Aims: Biomarkers may provide insights into molecular mechanisms underlying heart remodelling and dysfunction. Using a targeted proteomic approach, we aimed to identify circulating biomarkers associated with early stages of heart failure.
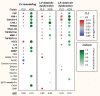
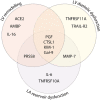
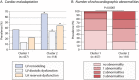
Methods and results: A total of 575 community-based participants (mean age, 57 years; 51.7% women) underwent echocardiography and proteomic profiling (CVD II panel, Olink Proteomics). We applied partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) and a machine learning algorithm [eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost)] to identify key proteins associated with echocardiographic abnormalities. We used Gaussian mixture modelling for unbiased clustering to construct phenogroups based on influential proteins in PLS-DA and XGBoost. Of 87 proteins, 13 were important in PLS-DA and XGBoost modelling for detection of left ventricular remodelling, left ventricular diastolic dysfunction, and/or left atrial reservoir dysfunction: placental growth factor, kidney injury molecule-1, prostasin, angiotensin-converting enzyme-2, galectin-9, cathepsin L1, matrix metalloproteinase-7, tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily members 10A, 10B, and 11A, interleukins 6 and 16, and α1-microglobulin/bikunin precursor. Based on these proteins, the clustering algorithm divided the cohort into two distinct phenogroups, with each cluster grouping individuals with a similar protein profile. Participants belonging to the second cluster (n = 118) were characterized by an unfavourable cardiovascular risk profile and adverse cardiac structure and function. The adjusted risk of presenting echocardiographic abnormalities was higher in this phenogroup than in the other (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: We identified proteins related to renal function, extracellular matrix remodelling, angiogenesis, and inflammation to be associated with echocardiographic signs of early-stage heart failure. Proteomic phenomapping discriminated individuals at high risk for cardiac remodelling and dysfunction.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Early-stage heart failure; Echocardiography; Epidemiology; Proteomics.
© 2021 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Cauwenberghs N, Knez J, D'hooge J, Thijs L, Yang W‐Y, Wei F‐F, Zhang Z‐Y, Staessen JA, Kuznetsova T. Longitudinal changes in LV structure and diastolic function in relation to arterial properties in general population. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2017; 10: 1307–1316. - PubMed
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DEJ, Drazner MH, Fonarow GC, Geraci SA, Horwich T, Januzzi JL, Johnson MR, Kasper EK, Levy WC, Masoudi FA, McBride PE, McMurray JJV, Mitchell JE, Peterson PN, Riegel B, Sam F, Stevenson LW, Tang WHW, Tsai EJ, Wilkoff BL. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013; 62: e147–e239. - PubMed
-
- Lieb W, Xanthakis V, Sullivan LM, Aragam J, Pencina MJ, Larson MG, Benjamin EJ, Vasan RS. Longitudinal tracking of left ventricular mass over the adult life course: clinical correlates of short‐ and long‐term change in the Framingham offspring study. Circulation United States 2009; 119: 3085–3092. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cauwenberghs N, Haddad F, Sabovčik F, Kobayashi Y, Amsallem M, Morris DA, Voigt JU, Kuznetsova T. Subclinical left atrial dysfunction profiles for prediction of cardiac outcome in the general population. J Hypertens 2020; 38: 2465–2474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

