Metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic modifications on the path to cancer
- PMID: 34050894
- PMCID: PMC9243210
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-021-00846-7
Metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic modifications on the path to cancer
Abstract
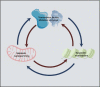
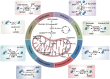
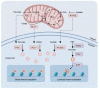
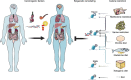
Metabolic rewiring and epigenetic remodeling, which are closely linked and reciprocally regulate each other, are among the well-known cancer hallmarks. Recent evidence suggests that many metabolites serve as substrates or cofactors of chromatin-modifying enzymes as a consequence of the translocation or spatial regionalization of enzymes or metabolites. Various metabolic alterations and epigenetic modifications also reportedly drive immune escape or impede immunosurveillance within certain contexts, playing important roles in tumor progression. In this review, we focus on how metabolic reprogramming of tumor cells and immune cells reshapes epigenetic alterations, in particular the acetylation and methylation of histone proteins and DNA. We also discuss other eminent metabolic modifications such as, succinylation, hydroxybutyrylation, and lactylation, and update the current advances in metabolism- and epigenetic modification-based therapeutic prospects in cancer.
Keywords: cancer therapy; epigenetics; metabolic reprogramming; tumor immunity; tumorigenesis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Adams RR, Maiato H, Earnshaw WC, Carmena M. Essential roles of Drosophila inner centromere protein (INCENP) and aurora B in histone H3 phosphorylation, metaphase chromosome alignment, kinetochore disjunction, and chromosome segregation. J Cell Biol. 2001;153:865–879. doi: 10.1083/jcb.153.4.865. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

