Comparison of outcomes in HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 34051225
- PMCID: PMC8152212
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.05.020
Comparison of outcomes in HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients with COVID-19
Abstract
Background: South Africa has the highest prevalence of HIV in the world and to date has recorded the highest number of cases of COVID-19 in Africa. There is uncertainty as to what the significance of this dual infection is, and whether people living with HIV (PLWH) have worse outcomes compared to HIV-negative patients with COVID-19. This study compared the outcomes of COVID-19 in a group of HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients admitted to a tertiary referral centre in Johannesburg, South Africa.
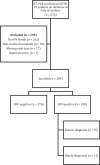
Methods: Data was collected on all adult patients with known HIV status and COVID-19, confirmed by reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), admitted to the medical wards and intensive care unit (ICU) between 6 March and 11 September 2020. The data included demographics, co-morbidities, laboratory results, severity of illness scores, complications and mortality, and comparisons were made between the HIV-positive and HIV negative groups.
Results: Three-hundred and eighty-four patients, 108 HIV-positive and 276 HIV-negative, were included in the study. Median 4C score was significantly higher in the HIV-positive patients compared to the HIV-negative patients, but there was no significant difference in mortality between the HIV-positive and HIV-negative groups (15% vs 20%, p = 0.31). In addition, HIV-positive patients who died were younger than their HIV-negative counterparts, but this was not statistically significant (47.5 vs 57 years, p = 0.06).
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that HIV is not a risk factor for moderate or severe COVID-19 disease neither is it a risk factor for mortality. However, HIV-positive patients with COVID-19 requiring admission to hospital are more likely to be younger than their HIV-negative counterparts. These findings need to be confirmed in future, prospective, studies.
Keywords: COVID-19; HIV; Mortality; South Africa.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Similar humoral immune responses against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in HIV and non-HIV individuals after COVID-19.J Infect. 2022 Mar;84(3):418-467. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.11.002. Epub 2021 Nov 6. J Infect. 2022. PMID: 34752819 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
SARS-CoV-2 humoral and cellular immune responses in COVID-19 convalescent individuals with HIV.J Infect. 2022 Sep;85(3):334-363. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2022.05.026. Epub 2022 May 27. J Infect. 2022. PMID: 35636532 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Coronavirus Update (Live): 100,907,153 Cases and 2,169,285 Deaths from COVID-19 Virus Pandemic - Worldometer. Available at https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/#countries. Accessed January 27, 2021, n.d.
-
- AIDSinfo | UNAIDS. Available at https://aidsinfo.unaids.org/. Accessed August 14, 2020, n.d.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical