Cyclin E in normal physiology and disease states
- PMID: 34052101
- PMCID: PMC8364501
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2021.05.001
Cyclin E in normal physiology and disease states
Abstract
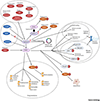
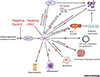
E-type cyclins, collectively called cyclin E, represent key components of the core cell cycle machinery. In mammalian cells, two E-type cyclins, E1 and E2, activate cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) and drive cell cycle progression by phosphorylating several cellular proteins. Abnormally elevated activity of cyclin E-CDK2 has been documented in many human tumor types. Moreover, cyclin E overexpression mediates resistance of tumor cells to various therapeutic agents. Recent work has revealed that the role of cyclin E extends well beyond cell proliferation and tumorigenesis, and it may regulate a diverse array of physiological and pathological processes. In this review, we discuss these various cyclin E functions and the potential for therapeutic targeting of cyclin E and cyclin E-CDK2 kinase.
Keywords: CDK2; cancer; cell cycle; cyclin E; cyclin-dependent kinases.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests P.S. has been a consultant to Novartis, Genovis, Guidepoint, The Planning Shop, ORIC Pharmaceuticals, Cedilla Therapeutics, Syros Pharmaceuticals, and Exo Therapeutics; his laboratory has received research funding from Novartis.
Figures

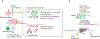
Similar articles
-
Kinase-independent function of E-type cyclins in liver cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jan 30;115(5):1015-1020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1711477115. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29339491 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Landscape of Tissue-Specific Cyclin E Functions in Vivo.PLoS Genet. 2016 Nov 9;12(11):e1006429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006429. eCollection 2016 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27828963 Free PMC article.
-
The requirement for cyclin E in c-Myc overexpressing breast cancers.Cell Cycle. 2020 Oct;19(20):2589-2599. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1804720. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 32975478 Free PMC article.
-
[Molecular mechanisms controlling the cell cycle: fundamental aspects and implications for oncology].Cancer Radiother. 2001 Apr;5(2):109-29. doi: 10.1016/s1278-3218(01)00087-7. Cancer Radiother. 2001. PMID: 11355576 Review. French.
-
E- and A-type cyclins as markers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2003 Sep;3(5):617-33. doi: 10.1586/14737159.3.5.617. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2003. PMID: 14510182 Review.
Cited by
-
High expression of centromere protein N as novel biomarkers for gastric adenocarcinoma.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023 Apr;6(4):e1798. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1798. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 36916294 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of G1 phase kinetics on the acquisition of stemness in cancer cells: the critical role of cyclin D.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Feb 14;52(1):230. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10351-3. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39951181 Review.
-
Targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) interactions with cyclins and Speedy 1 (Spy1) for cancer and male contraception.Future Med Chem. 2025 Mar;17(5):607-627. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2025.2463868. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Future Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40034037 Review.
-
Cyclosporine A causes gingival overgrowth via reduced G1 cell cycle arrest in gingival fibroblasts.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 20;19(12):e0309189. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309189. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39705288 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxyzine Induces Cell Death in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells via Mitochondrial Superoxide and Modulation of Jak2/STAT3 Signaling.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2022 Nov 1;30(6):585-592. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2022.121. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2022. PMID: 36305293 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

