Mortality and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia treated with non-invasive respiratory support: A rapid review
- PMID: 34052780
- PMCID: PMC8137355
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2021.05.007
Mortality and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia treated with non-invasive respiratory support: A rapid review
Abstract
Introduction and aim: Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) have been widely employed to treat acute respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19 pneumonia, but their role in terms of efficacy and safety are still debated. The aim of this review was to analyse mortality and intubation rates in COVID-19 patients treated with NIV/CPAP.
Methods: Rapid review methodology was applied to include all the studies published since December-2019 until November-2020 with available data on in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients treated with NIV or CPAP.
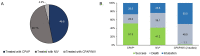
Results: 23 manuscripts were included (4776 patients, 66% males, 46% with hypertension). 46% of patients received non-invasive respiratory support, of which 48.4% with CPAP, 46% with NIV, and 4% with either CPAP or NIV. Non-invasive respiratory support failed in 47.7% of patients, of which 26.5% were intubated and 40.9% died. In-hospital mortality was higher in patients treated with NIV compared with CPAP (35.1% vs. 22.2%). Complications were under-reported, but mostly not related to CPAP/NIV treatment.
Conclusion: CPAP and NIV appear equally and frequently applied in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, but associated with high mortality. Robust evidence is urgently needed to confirm the clinical efficacy of non-invasive respiratory support in COVID-19-related ARDS.
Keywords: COVID-19; Continuous positive airway pressure; Intubation; Mortality; Non-invasive ventilation; Respiratory failure.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in regard to the present manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Coronavirus Disease Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/?gclid=Cj0KCQiA962BBhCzARIsAIpWEL1udlQP7Cy_xp9BE... Updated on 16 February 2021 [accessed 16 February 2021]
-
- Santus P., Radovanovic D., Saderi L., Marino P., Cogliati C., De Filippis G., et al. Severity of respiratory failure at admission and in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19: a prospective observational multicentre study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(10) doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-043651. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

