Chemical composition and potentiating action of Norfloxacin mediated by the essential oil of Piper caldense C.D.C. against Staphylococcus aureus strains overexpressing efflux pump genes
- PMID: 34052872
- PMCID: PMC8164493
- DOI: 10.1007/s00203-021-02393-5
Chemical composition and potentiating action of Norfloxacin mediated by the essential oil of Piper caldense C.D.C. against Staphylococcus aureus strains overexpressing efflux pump genes
Abstract
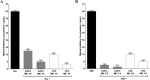
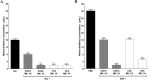
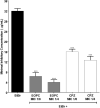
Infectious diseases caused by multidrug-resistant microorganisms has increased in the last years. Piper species have been reported as a natural source of phytochemicals that can help in combating fungal and bacterial infections. This study had as objectives characterize the chemical composition of the essential oil from Piper caldense (EOPC), evaluate its potential antimicrobial activity, and investigate the synergistic effect with Norfloxacin against multidrug-resistant S. aureus overproducing efflux pumps, as well as, verify the EOPC ability to inhibit the Candida albicans filamentation. EOPC was extracted by hydrodistillation, and the chemical constituents were identified by gas chromatography, allowing the identification of 24 compounds (91.9%) classified as hydrocarbon sesquiterpenes (49.6%) and oxygenated sesquiterpenes (39.5%). Antimicrobial tests were performed using a 96-well plate microdilution method against C. albicans ATCC 10231, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 standard strains, as well as against multidrug-resistant strains S. aureus SA1199B (overexpressing norA gene), S. aureus K2068 (overexpressing mepA gene) and S. aureus K4100 (overexpressing qacC gene). The oil showed activity against C. albicans ATCC 10231 (≥ 512 µg/mL) and was able to inhibit hyphae formation, an important mechanism of virulence of C. albicans. On the other hand, EOPC was inactive against all bacterial strains tested (≤ 1,024 µg mL). However, when combined with Norfloxacin at subinhibitory concentration EOPC reduced the Norfloxacin and Ethidium bromide MIC values against S. aureus strains SA1199B, K2068 and K4100. These results indicate that EOPC is a source of phytochemicals acting as NorA, MepA and QacC inhibitors.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Antifungal; Efflux pump inhibitors; Essential oil; Fungal dimorphism; Piper caldense.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial activity of Mimosa caesalpiniifolia Benth and its interaction with antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus strains overexpressing efflux pump genes.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2019 Jul;69(1):57-63. doi: 10.1111/lam.13163. Epub 2019 May 15. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31002429
-
Unlocking bacterial defense: Exploring the potent inhibition of NorA efflux pump by coumarin derivatives in Staphylococcus aureus.Microb Pathog. 2024 May;190:106608. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106608. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38503396
-
Chemical composition of Piper gaudichaudianum Kunth essential oil and evaluation of its antimicrobial and modulatory effects on antibiotic resistance, antibiofilm, and cell dimorphism inhibitory activities.3 Biotech. 2023 Jul;13(7):255. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03681-1. Epub 2023 Jun 29. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37396469 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiating activity of Norfloxacin by synthetic chalcones against NorA overproducing Staphylococcus aureus.Microb Pathog. 2021 Jun;155:104894. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104894. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Microb Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33894291 Review.
-
An Update on Staphylococcus aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(24):2168-2185. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200704135837. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32621719 Review.
Cited by
-
Current State of Knowledge Regarding WHO High Priority Pathogens-Resistance Mechanisms and Proposed Solutions through Candidates Such as Essential Oils: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 4;24(11):9727. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119727. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298678 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Activity of the Essential Oil of Piper tuberculatum Jacq. Fruits against Multidrug-Resistant Strains: Inhibition of Efflux Pumps and β-Lactamase.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jun 19;12(12):2377. doi: 10.3390/plants12122377. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37376002 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of Aromatic Plant-Derived Essential Oils for the Control of Foodborne Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance in Animal Production: A Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Nov 21;11(11):1673. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111673. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Essential Oils in the Inhibition of Efflux Pumps and Reversion of Bacterial Resistance to Antimicrobials.Curr Microbiol. 2021 Oct;78(10):3609-3619. doi: 10.1007/s00284-021-02635-1. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Curr Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34432112 Review.
-
The Major Facilitator Superfamily and Antimicrobial Resistance Efflux Pumps of the ESKAPEE Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Feb 7;12(2):343. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020343. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830254 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barbedo LS, Sgarbi DBG. Candidíase. DST-J Brasileiro De Doenças Sex Transm. 2010;22:22–38.
-
- Bezerra JWAB, Rodrigues FC, Da Cruz RP et al (2020) Antibiotic Potential and Chemical Composition of the Essential Oil of Piper caldense C. DC. (Piperaceae). Appl Sci 10:631
-
- Cardozo Júnior EL, Chaves MCO. Caldensin, a new natural n-Methylaristolactam from Piper caldense. Pharm Biol. 2003;41:216–218. doi: 10.1076/phbi.41.3.216.15091. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

