Peri-anastomotic microdialysis lactate assessment after esophagectomy
- PMID: 34052933
- PMCID: PMC8387264
- DOI: 10.1007/s10388-021-00846-w
Peri-anastomotic microdialysis lactate assessment after esophagectomy
Abstract
Background: Esophagectomy is the cornerstone in curative treatment for esophageal and gastroesophageal junctional cancer. Esophageal resection is an advanced procedure with many complications, whereof anastomotic leak is the most dreaded. This study aimed to monitor the microcirculation with microdialysis analysis of local lactate levels in real-time on both sides of the esophagogastric anastomosis in totally minimally invasive Ivor-Lewis esophagectomy.
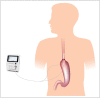
Materials and methods: Twenty-five patients planned for esophageal resection with gastric conduit reconstruction and intrathoracic anastomosis were recruited. A sampling device, the OnZurf® Probe, along with the CliniSenz® Analyser (Senzime AB, Uppsala Sweden) was utilized for measurements. Lactate levels from both sides of the anastomosis were analysed in real time, on site, by a transportable analyser device. Measurements were made every 30 min during the first 24 h, and thereafter every 2 hours for up to 4 days.
Results: All probes could be positioned as planned and on the third postoperative day 19/25 and 15/25 of the esophageal and gastric probes, respectively, continued to deliver measurements. In total, 89.6% (1539/1718) and 72.4% (1098/1516) of the measurements were deemed successful. The average lactate level on the esophageal side of the anastomosis and the gastric conduit ranged between 1.1-11.5 and 0.8-7.0 mM, respectively. Two anastomotic leaks occurred, one of which had persisting high lactate levels on the gastric side of the anastomosis.
Conclusion: Application and use of the novel CliniSenz® analyser system, in combination with the OnZurf® Probe was feasible and safe. Continuous monitoring of analytes from the perianastomotic area has the potential to improve care after esophageal resection.
Keywords: Anastomotic leak; Esophagus; Microdialysis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Figures
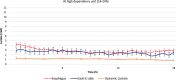
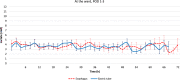
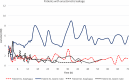
 ), visible already during the first postoperative hours. Note the marked increase in lactate in the gastric tube of this patient compared to the remaining measurements illustrated in Figs. 2 and 3
), visible already during the first postoperative hours. Note the marked increase in lactate in the gastric tube of this patient compared to the remaining measurements illustrated in Figs. 2 and 3References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer, C., C. Fitzmaurice, T.F. Akinyemiju, et al., Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years for 29 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol, 2018. 4(11): p. 1553–1568. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
