Novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV (COVID-19): early estimation of epidemiological parameters and epidemic size estimates
- PMID: 34053269
- PMCID: PMC8165596
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2020.0265
Novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV (COVID-19): early estimation of epidemiological parameters and epidemic size estimates
Abstract
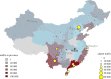
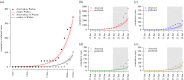
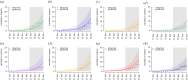
Since it was first identified, the epidemic scale of the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in Wuhan, China, has increased rapidly, with cases arising across China and other countries and regions. Using a transmission model, we estimate a basic reproductive number of 3.11 (95% CI, 2.39-4.13), indicating that 58-76% of transmissions must be prevented to stop increasing. We also estimate a case ascertainment rate in Wuhan of 5.0% (95% CI, 3.6-7.4). The true size of the epidemic may be significantly greater than the published case counts suggest, with our model estimating 21 022 (prediction interval, 11 090-33 490) total infections in Wuhan between 1 and 22 January. We discuss our findings in the light of more recent information. This article is part of the theme issue 'Modelling that shaped the early COVID-19 pandemic response in the UK'.
Keywords: China; SARS-CoV-2; ascertainment rate; international travel; pandemic; transmission model.
Figures
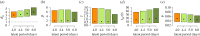
References
-
- Gorbalenya AE, et al. . 2020. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: the species and its viruses—a statement of the Coronavirus Study Group. bioRxiv 2020.02.07.937862. (10.1101/2020.02.07.937862) - DOI
-
- World Health Organization. 2020. Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) situation report. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization.
-
- World Health Organization. 2020. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
