Adjuvant therapy using ex vivo-expanded allogenic natural killer cells in hepatectomy patients with hepatitis B virus related solitary hepatocellular carcinoma: MG4101 study
- PMID: 34053923
- PMCID: PMC8180393
- DOI: 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.2.206
Adjuvant therapy using ex vivo-expanded allogenic natural killer cells in hepatectomy patients with hepatitis B virus related solitary hepatocellular carcinoma: MG4101 study
Abstract
Backgrounds/aims: Fewer reports have been published regarding hepatectomy patients with solitary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who received immunotherapeutic agents as adjuvant therapy. We evaluated the safety and efficacy of ex vivo-expanded allogenic natural killer (NK) cells in those patients with modified International Union Against Cancer (UICC) stage T3.
Methods: From August 2014 to October 2015, five patients who underwent hepatic resection received ex vivo-expanded allogenic NK cells. Patients received five rounds of NK cells (2-3×107 cells/kg) at postoperative 4, 6, 8, 12, and 16 weeks. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT02008929.
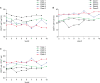
Results: The median age of the five patients (three men and two women) was 44.8 years (range, 36-54 years). All had hepatitis B virus-related HCC, and the median tumor size was 2.2 cm (range, 2.1-8.2 cm). None of the patients had any adverse events. HCC recurrence developed in two patients at one year after hepatic resection, but four patients were alive at 3 years. The two recurrence-free patients showed a higher ratio of CD8+ T lymphocyte populations before and after administration of ex vivo-expanded allogenic NK cells compared with the three patients who experienced recurrence.
Conclusions: Immunotherapy using ex vivo-expanded allogenic NK cells in hepatectomy patients can be used safely. Further studies should be investigated for efficacy.
Keywords: Efficacy; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Immunotherapy; Natural killer cells; Safety.
Conflict of interest statement
Sung Yoo Cho, Miyoung Jung, Jung Hyun Her, Okjae Lim, and Yu-Kyeong Hwang are GC LabCell employees. All remaining authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Adjuvant immunotherapy with autologous cytokine-induced killer cells for hepatocellular carcinoma.Gastroenterology. 2015 Jun;148(7):1383-91.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.02.055. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Gastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 25747273 Clinical Trial.
-
Adoptive Transfer of Autologous Invariant Natural Killer T Cells as Immunotherapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Phase I Clinical Trial.Oncologist. 2021 Nov;26(11):e1919-e1930. doi: 10.1002/onco.13899. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Oncologist. 2021. PMID: 34255901 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical efficacy of postoperative adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization on hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Apr 2;14:100. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0855-z. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27038790 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Killer Cells and T Cells in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Viral Hepatitis: Current Status and Perspectives for Future Immunotherapeutic Approaches.Cells. 2021 May 28;10(6):1332. doi: 10.3390/cells10061332. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34071188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interactions between major immune effector cells and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A systematic review.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Dec;101(Pt A):108220. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108220. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34673334
Cited by
-
Recent Progress in Systemic Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 19;25(2):1259. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021259. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neoadjuvant Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022 Aug 31;9:929-946. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S357313. eCollection 2022. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022. PMID: 36068876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A spreadable self-gelling hemostatic powder sensitizes CAR-NK cell therapy to prevent hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence postresection.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 16;23(1):353. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03424-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40380326 Free PMC article.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
