β-Caryophyllene, A Natural Dietary CB2 Receptor Selective Cannabinoid can be a Candidate to Target the Trinity of Infection, Immunity, and Inflammation in COVID-19
- PMID: 34054510
- PMCID: PMC8163236
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.590201
β-Caryophyllene, A Natural Dietary CB2 Receptor Selective Cannabinoid can be a Candidate to Target the Trinity of Infection, Immunity, and Inflammation in COVID-19
Abstract
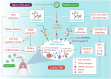
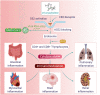
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19), caused by novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is an ongoing pandemic and presents a public health emergency. It has affected millions of people and continues to affect more, despite tremendous social preventive measures. Identifying candidate drugs for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is crucial. The pathogenesis and the complications with advanced infection mainly involve an immune-inflammatory cascade. Therefore, therapeutic strategy relies on suppressing infectivity and inflammation, along with immune modulation. One of the most promising therapeutic targets for the modulation of immune-inflammatory responses is the endocannabinoid system, particularly the activation of cannabinoid type 2 receptors (CB2R), a G-protein coupled receptor which mediates the anti-inflammatory properties by modulating numerous signaling pathways. To pharmacologically activate the CB2 receptors, a naturally occurring cannabinoid ligand, beta-caryophyllene (BCP), received attention due to its potent anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and immunomodulatory properties. BCP is recognized as a full selective functional agonist on CB2 receptors and produces therapeutic effects by activating CB2 and the nuclear receptors, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs). BCP is regarded as the first dietary cannabinoid with abundant presence across cannabis and non-cannabis plants, including spices and other edible plants. BCP showed tissue protective properties and favorably modulates numerous signaling pathways and inhibits inflammatory mediators, including cytokines, chemokines, adhesion molecules, prostanoids, and eicosanoids. Based on its pharmacological properties, molecular mechanisms, and the therapeutic potential of BCP as an immunomodulator, anti-inflammatory, organ-protective, and antiviral, we hypothesize that BCP could be a promising therapeutic and/or preventive candidate to target the triad of infection, immunity, and inflammation in COVID-19. In line with numerous studies that proposed the potential of cannabinoids in COVID-19, BCP may be a novel candidate compound for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical development due to its unique functional receptor selectivity, wide availability and accessibility, dietary bioavailability, nonpsychoactivity, and negligible toxicity along with druggable properties, including favorable pharmacokinetic and physicochemical properties. Based on reasonable pharmacological mechanisms and therapeutic properties, we speculate that BCP has potential to be investigated against COVID-19 and will inspire further preclinical and clinical studies.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; beta-caryophyllene; immunomodulators; natural products.
Copyright © 2021 Jha, Sharma, Hashiesh, Arunachalam, Meeran, Javed, Patil, Goyal and Ojha.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A focused review on CB2 receptor-selective pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential of β-caryophyllene, a dietary cannabinoid.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Aug;140:111639. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111639. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34091179 Review.
-
CB2 receptor-selective agonists as candidates for targeting infection, inflammation, and immunity in SARS-CoV-2 infections.Drug Dev Res. 2021 Feb;82(1):7-11. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21752. Epub 2020 Nov 15. Drug Dev Res. 2021. PMID: 33190277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can limonene be a possible candidate for evaluation as an agent or adjuvant against infection, immunity, and inflammation in COVID-19?Heliyon. 2020 Dec 11;7(1):e05703. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05703. eCollection 2021 Jan. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33490659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of β-Caryophyllene: A Dietary Cannabinoid in Diabetes and Associated Complications.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 28;12(10):2963. doi: 10.3390/nu12102963. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32998300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can Echinacea be a potential candidate to target immunity, inflammation, and infection - The trinity of coronavirus disease 2019.Heliyon. 2021 Feb;7(2):e05990. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e05990. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33585706 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
β-Caryophyllene Acts as a Ferroptosis Inhibitor to Ameliorate Experimental Colitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 16;23(24):16055. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416055. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555694 Free PMC article.
-
The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in the modulation of hyperinflammation induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection: A perspective for COVID-19 therapy.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 17;14:1127358. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1127358. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36875108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enzymatic and Microwave Pretreatments and Supercritical CO2 Extraction for Improving Extraction Efficiency and Quality of Origanum vulgare L. spp. hirtum Extracts.Plants (Basel). 2021 Dec 25;11(1):54. doi: 10.3390/plants11010054. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35009059 Free PMC article.
-
A review of natural products, their effects on SARS-CoV-2 and their utility as lead compounds in the discovery of drugs for the treatment of COVID-19.Med Chem Res. 2022;31(1):40-51. doi: 10.1007/s00044-021-02826-2. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Med Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 34873386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights in Natural Bioactive Compounds for Periodontal Disease: Advanced Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential.Molecules. 2025 Feb 10;30(4):807. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040807. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005119 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alberti T. B., Marcon R., Bicca M. A., Raposo N. R. B., Calixto J. B., Dutra R. C. (2014). Essential Oil from Pterodon emarginatus Seeds Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Modulating Th1/Treg Cell Balance. J. Ethnopharmacol. 155, 485–494. 10.1016/j.jep.2014.05.044 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

