Modulation of Pathological Pain by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
- PMID: 34054523
- PMCID: PMC8149758
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.642820
Modulation of Pathological Pain by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
Abstract
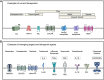
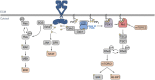
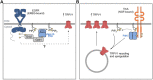
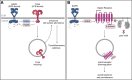
Chronic pain has been widely recognized as a major public health problem that impacts multiple aspects of patient quality of life. Unfortunately, chronic pain is often resistant to conventional analgesics, which are further limited by their various side effects. New therapeutic strategies and targets are needed to better serve the millions of people suffering from this devastating disease. To this end, recent clinical and preclinical studies have implicated the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway in chronic pain states. EGFR is one of four members of the ErbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases that have key roles in development and the progression of many cancers. EGFR functions by activating many intracellular signaling pathways following binding of various ligands to the receptor. Several of these signaling pathways, such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, are known mediators of pain. EGFR inhibitors are known for their use as cancer therapeutics but given recent evidence in pilot clinical and preclinical investigations, may have clinical use for treating chronic pain. Here, we review the clinical and preclinical evidence implicating EGFR in pathological pain states and provide an overview of EGFR signaling highlighting how EGFR and its ligands drive pain hypersensitivity and interact with important pain pathways such as the opioid system.
Keywords: animal models; epidermai growth factor receptor; inflammation; membrane traffic; neuropathic pain; receptor tyrosine kinase.
Copyright © 2021 Borges, Mekhail, Fairn, Antonescu and Steinberg.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Small molecule inhibitors targeting the EGFR/ErbB family of protein-tyrosine kinases in human cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Jan;139:395-411. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.11.014. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 30500458 Review.
-
The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer.Pharmacol Res. 2014 Jan;79:34-74. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Pharmacol Res. 2014. PMID: 24269963 Review.
-
Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Its Ligands in Kidney Inflammation and Damage.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Dec 23;2018:8739473. doi: 10.1155/2018/8739473. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 30670929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015 Sep;5(5):390-401. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015. PMID: 26579470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth hormone-induced phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor in 3T3-F442A cells. Modulation of EGF-induced trafficking and signaling.J Biol Chem. 2003 May 23;278(21):18902-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300939200. Epub 2003 Mar 14. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12642595
Cited by
-
Treatment of Painful Palmoplantar Keratoderma Related to Pachyonychia Congenita Using EGFR Inhibitors.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 3;10(4):841. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040841. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453591 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanism of Gelsemium elegans (Gardner and Champ.) Benth. Against Neuropathic Pain Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Evidence.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 3;12:792932. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.792932. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35046814 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic insights into mental health status: plasma markers in young adults.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Jan 24;14(1):55. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-02751-z. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38267423 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of secreted phosphoprotein 1 attenuates sciatic nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain: Regulating extracellular signal-regulated kinase and neuroinflammatory signaling pathways.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Feb;12(2):e1132. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1132. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 38415922 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing EGFR Inhibitors for Oral Cancer Pain and Opioid Tolerance.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 3;16(11):1558. doi: 10.3390/ph16111558. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004424 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alkislar I., Miller A. R., Hohmann A. G., Sadaka A. H., Cai X., Kulkarni P., et al. (2020). Inhaled Cannabis Suppresses Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Nociception by Decoupling the Raphe Nucleus: A Functional Imaging Study in Rats. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 6, 479–489. 10.1016/j.bpsc.2020.11.015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

