Guhong Injection Protects Against Apoptosis in Cerebral Ischemia by Maintaining Cerebral Microvasculature and Mitochondrial Integrity Through the PI3K/AKT Pathway
- PMID: 34054531
- PMCID: PMC8155598
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.650983
Guhong Injection Protects Against Apoptosis in Cerebral Ischemia by Maintaining Cerebral Microvasculature and Mitochondrial Integrity Through the PI3K/AKT Pathway
Abstract
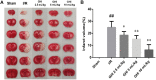
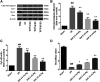
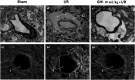
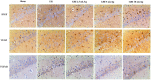
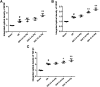
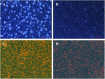
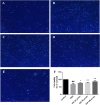
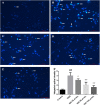
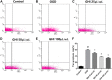
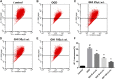
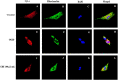
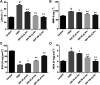
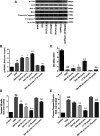
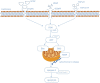
Guhong injection (GHI) can be used for the treatment of ischemic stroke. We investigated the antiapoptotic activity of GHI, its ability to repair the cerebral microvessels and mitochondria, and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway of GHI against cerebral ischemia. Western blot and immunohistochemical analyses were used to determine the expression of cleaved caspase-3, B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2), cytochrome c (Cyt-c), basic fibroblast growth factor (BFGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), and proteins in the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy were used to evaluate the structures of the cerebral microvasculature and cells. Hoechst 33342 staining was used to evaluate the nuclear morphology. FITC-AV/PI double staining was used to measure the antiapoptotic effects. The fluorescent dye JC-1 was used to measure mitochondrial membrane potential. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to detect the activities of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Biochemical assay kits were used to detect the activities of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and malondialdehyde (MDA). Compared with the middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) group, there was decreased infarct volume and significantly improved neurological deficits in the GHI group. In addition, the expression of Bcl-2 was significantly upregulated, while the expression of Cyt-c, Bax, and cleaved caspase-3 was notably downregulated. GHI administration attenuated the pathological change and morphology of the cerebral microvasculature, and immunohistochemical staining indicated that the expressions of BFGF, VEGF, and TGF-β1 were significantly increased. The cell morphology, cell viability, cell nuclei characteristics, and mitochondrial morphology normalized following GHI treatment, which decreased the release of Cyt-c and the mitochondrial membrane potential. The levels of LDH, MMP-9, and MDA decreased, while SOD increased. Moreover, GHI administration inhibited the activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in rat brain microvascular endothelial cells (rBMECs) following oxygen/glucose deprivation (OGD) injury. Therefore, our results show that GHI administration resulted in antiapoptosis of cerebral cells and repair of cerebral microvessels and mitochondria via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Keywords: Guhong injection; PI3K/Akt pathway; antiapoptosis; cerebral microvascular; ischemic stroke; mitochondria.
Copyright © 2021 Zhou, He, Zhu, Lin, Chen, Shao, Wan and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
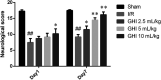

Similar articles
-
Chemical composition, pharmacology and pharmacokinetic studies of GuHong injection in the treatment of ischemic stroke.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 7;14:1261326. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1261326. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37745083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effect of Naoxintong Capsule () Combined with Guhong Injection () on Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells during Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Chin J Integr Med. 2021 Oct;27(10):744-751. doi: 10.1007/s11655-020-3215-3. Epub 2020 Apr 4. Chin J Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 32248514
-
Geniposide Prevents Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Apoptosis in H9c2 Cells: Improvement of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Activation of GLP-1R and the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(1):407-21. doi: 10.1159/000445634. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27372651
-
Arctium lappa L. roots ameliorates cerebral ischemia through inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and suppressing AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy.Phytomedicine. 2021 May;85:153526. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153526. Epub 2021 Feb 21. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33691269
-
Ameliorating effects of traditional Chinese medicine preparation, Chinese materia medica and active compounds on ischemia/reperfusion-induced cerebral microcirculatory disturbances and neuron damage.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015 Jan;5(1):8-24. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2014.11.002. Epub 2015 Jan 24. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015. PMID: 26579420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Saquayamycin B1 Suppresses Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration by Inhibiting PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells.Mar Drugs. 2022 Sep 7;20(9):570. doi: 10.3390/md20090570. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36135759 Free PMC article.
-
BNIP3 mediates the different adaptive responses of fibroblast-like synovial cells to hypoxia in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.Mol Med. 2022 Jun 11;28(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00490-9. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35690741 Free PMC article.
-
Irisin protects against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in a SIRT3-dependent manner.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 1;16:1558457. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1558457. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40235548 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in pathogenesis and treatment of vascular endothelial injury-related diseases mediated by mitochondrial abnormality.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 30;15:1422686. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1422686. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39281286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical composition, pharmacology and pharmacokinetic studies of GuHong injection in the treatment of ischemic stroke.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 7;14:1261326. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1261326. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37745083 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Rahman R. F., Alqasoumi S. I., Ogaly H. A., Abd-Elsalam R. M., El-Banna H. A., Soliman G. A. (2020). Propolis ameliorates cerebral injury in focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) rat model via upregulation of TGF-β1. Saudi Pharm. J. 28, 116–126. 10.1016/j.jsps.2019.11.013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen J. K., Wan H. T., Zhou H. F., Peng X. Q., He Y. (2016). Correlation study on in vivo pharmacokinetics and anti-oxidation of Guhong injection in cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury model of rats. Chin. Tradit. Herbal Drugs. 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2016.03.016 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

