Pathogenesis and Function of Interleukin-35 in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 34054534
- PMCID: PMC8155723
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.655114
Pathogenesis and Function of Interleukin-35 in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
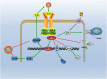
It is well known that RA (Rheumatoid arthritis) is an autoimmune disease characterized by multiple and symmetric arthropathy. The main pathological features of RA are synovial hyperplasia, angiogenesis, pannus formation, inflammatory cell infiltration, articular cartilage, bone destruction, and ultimately joint dysfunction, even deformity. IL-35 (Interleukin-35) is a new member of the IL-12 (Interleukin-12) family, which is an immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory cytokine secreted mainly by Treg (T regulatory cells). There is evidence suggested that IL-35 can attenuate the progression of RA through influencing the immune and pathological process. It suggests that IL-35 played an important role in the pathogenesis of RA, and can be used as a potential target for the future treatment of RA. This review summarizes the recent advances of IL-35 in the pathological roles and the therapeutic potential roles in RA.
Keywords: IL-12 family; IL-35; Th17; article highlights; rheumatoid arthritis; treg.
Copyright © 2021 Xin, Jie, Cheng, Bin and Dan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Abdi E., Najafipour H., Joukar S., Dabiri S., Esmaeli-Mahani S., Abbasloo E., et al. (2018). Expression of IGF-1, IL-27 and IL-35 Receptors in Adjuvant Induced Rheumatoid Arthritis Model, Iran. J. Immunol., 15, 14–27. IJIv15i1A2 - PubMed
-
- Ally M. M. T. M., Hodkinson B., Meyer P. W. A., Musenge E., Tintinger G. R., Tikly M., et al. (2015). Circulating Anti-citrullinated Peptide Antibodies, Cytokines and Genotype as Biomarkers of Response to Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drug Therapy in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 16 (1), 130. 10.1186/s12891-015-0587-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

