CircRNA circ_0006677 Inhibits the Progression and Glycolysis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Sponging miR-578 and Regulating SOCS2 Expression
- PMID: 34054537
- PMCID: PMC8155686
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.657053
CircRNA circ_0006677 Inhibits the Progression and Glycolysis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Sponging miR-578 and Regulating SOCS2 Expression
Abstract
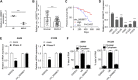
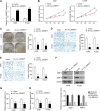
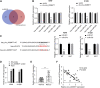
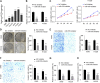
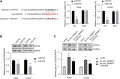
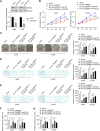
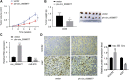
Objective: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been demonstrated in playing an important role in the physiological and pathological processes (such as cancer). This paper aims to clarify the role of Circ_0006677 in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression. Methods: Using clinical data and in vitro cell line models, we revealed the tumor-suppressive role of circ_0006677 in lung cancer. Using the online bioinformatics tool, we predicted the target of circ_0006677 and further validated its regulatory mechanisms responsible for its tumor suppressor function in NSCLC. Results: Circ_0006677 expression was reduced in NSCLC tissues of patients and lung cancer cells in comparison to adjacent normal tissues. Lower expression of circ_0006677 was significantly associated with poorer patient survival. Overexpression of circ_0006677 significantly inhibited the ability of NSCLC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and glycolysis. Mechanically, circ_0006677 could inhibit NSCLC progression and glycolysis by regulating the expression of the signal transducer inhibitor SOSC2 through sponging microRNA-578 (miR-578). Conclusion: Circ_0006677 prevents the progression of NSCLC via modulating the miR-578/SOSC2 axis.
Keywords: SOSC2; circ_0006677; lung cancer; microRNA-578; non–small-cell lung cancer.
Copyright © 2021 Yang, Zhao, Yao, Zong and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

