Shaoyao-Gancao Decoction Ameliorates the Inflammation State in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Rats via Remodeling Gut Microbiota and Suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway
- PMID: 34054541
- PMCID: PMC8155368
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.670054
Shaoyao-Gancao Decoction Ameliorates the Inflammation State in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Rats via Remodeling Gut Microbiota and Suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
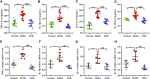
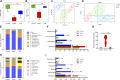
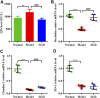
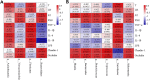
Background: Emerging evidence suggests that gut microbiota plays a vital role in the occurrence of multiple endocrine disorders including polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Shaoyao-Gancao Decoction (SGD), a classical Chinese prescription, has been widely used in the treatment of PCOS for decades. In previous studies, we found that SGD treatment could effectively reduce ovarian inflammation in PCOS rats. However, whether the anti-inflammation effect of SGD involves the regulation of the gut microbiota remains elusive. Methods: Letrozole-induced PCOS rat models were established, and the therapeutic effects of SGD were evaluated. Specifically, body weight, serum hormone concentrations, estrus phase and ovary histopathology were assessed. Then the structure of gut microbiota was determined by 16s rRNA sequencing. Additionally, the serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and LPS were measured by ELISA kits. The key gene and protein expressions of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway were detected by quantitative real-time PCR and western blot. Results: SGD could effectively reduce body weight, regulate estrous cycles and ameliorate hyperandrogenism in PCOS rats. In addition, SGD treatment decreased releases of pro-inflammatory cytokines, enhanced the expressions of tight junction (occludin and claudin1), and then prevented a translocation of LPS into bloodstream. SGD could significantly reduce the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes, decrease the abundance of LPS-producing pathogens Proteobateria and enrich the abundance of Butyricicoccus, Coprococcus, Akkermansia Blautia and Bacteroides in PCOS rats. Furthermore, SGD blunted the key gene and protein expressions of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway both in vivo and in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Conclusion: SGD administration could ameliorate the inflammatory response in PCOS rats by remodeling gut microbiome structure, protecting gut barrier, and suppressing TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: TLR4/NF-κB pathway; gut barrier; gut microbiota; polycystic ovary syndrome; shaoyao-gancao decoction.
Copyright © 2021 Chang, Deng, Shao, Xu, Zhao, Sun, Zhang, Hou and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Alanbay I., Ercan C. M., Sakinci M., Coksuer H., Ozturk M., Tapan S. (2012). A Macrophage Activation Marker Chitotriosidase in Women with PCOS: Does Low-Grade Chronic Inflammation in PCOS Relate to PCOS Itself or Obesity? Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 286, 1065–1071. 10.1007/s00404-012-2425-0 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

