Inflammatory Immune Cytokine TNF-α Modulates Ezrin Protein Activation via FAK/RhoA Signaling Pathway in PMVECs Hyperpermeability
- PMID: 34054551
- PMCID: PMC8152434
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.676817
Inflammatory Immune Cytokine TNF-α Modulates Ezrin Protein Activation via FAK/RhoA Signaling Pathway in PMVECs Hyperpermeability
Abstract
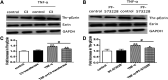
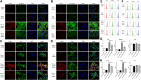
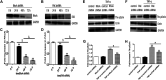
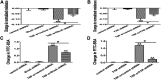
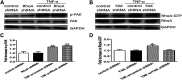
Background: One of the important pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is the dysfunction of pulmonary microvascular endothelial barrier induced by a hyperinflammatory immune response. However, the potential mechanisms of such an imbalance in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs) are not yet understood. Purpose: Explore the molecular mechanism of endothelial barrier dysfunction induced by inflammatory immune cytokines in ARDS, and find a therapeutic target for this syndrome. Methods: Rat PMVECs were cultured to form a monolayer. Immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, and Western blotting were selected to detect the distribution and the expression level of phosphorylated Ezrin protein and Ezrin protein. Transendothelial electrical resistance (TER) and transendothelial fluxes of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled bovine serum albumin (BSA) were utilized to measure the permeability of the cell monolayer. Ezrin short hairpin RNA (shRNA) and Ezrin 567-site threonine mutant (EzrinT567A) were used to examine the role of Ezrin protein and phosphorylated Ezrin protein in endothelial response induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), respectively. The function of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and Ras homolog gene family, member A (RhoA) signaling pathways were estimated by inhibitors and RhoA/FAK shRNA in TNF-α-stimulated rat PMVECs. The activation of FAK and RhoA was assessed by Western blotting or pull-down assay plus Western blotting. Results: The TER was decreased after TNF-α treatment, while the Ezrin protein phosphorylation was increased in a time- and dose-dependent manner. The phosphorylated Ezrin protein was localized primarily at the cell periphery, resulting in filamentous actin (F-actin) rearrangement, followed by a significant decrease in TER and increase in fluxes of FITC-BSA. Moreover, FAK and RhoA signaling pathways were required in the phosphorylation of Ezrin protein, and the former positively regulated the latter. Conclusion: The phosphorylated Ezrin protein was induced by TNF-α via the FAK/RhoA signaling pathway leading to endothelial hyperpermeability in PMVECs.
Keywords: Ezrin protein; acute respiratory distress syndrome; endothelial permeability; inflammatory immune response; molecular mechanism.
Copyright © 2021 Zhou, Jiang, Chen, Qian and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The handling editor declared a shared affiliation with the authors at time of review. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α requires Ezrin to regulate the cytoskeleton and cause pulmonary microvascular endothelial barrier damage.Microvasc Res. 2021 Jan;133:104093. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2020.104093. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Microvasc Res. 2021. PMID: 33007316 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase C-α signals P115RhoGEF phosphorylation and RhoA activation in TNF-α-induced mouse brain microvascular endothelial cell barrier dysfunction.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Apr 8;8:28. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-28. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21473788 Free PMC article.
-
[Role of Ezrin in the injury of rat pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells induced by tumor necrosis factor-α and the impact of Rac 1].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014 Nov;26(11):785-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.11.004. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014. PMID: 25399891 Chinese.
-
Phosphorylated ERM Mediates Lipopolysaccharide Induced Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells Permeability Through Negatively Regulating Rac1 Activity.Arch Bronconeumol (Engl Ed). 2019 Jun;55(6):306-311. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2018.09.014. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Arch Bronconeumol (Engl Ed). 2019. PMID: 30448045 English, Spanish.
-
[Role of adenosine A2b receptors in pulmonary microvascular endothelial inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Dec;31(12):1485-1490. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.12.010. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 32029034 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Scutellaria barbata D.Don extract regulates Ezrin-mediated triple negative breast cancer progress via suppressing the RhoA /ROCK1 signaling.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Mar 21;13(2):tfae033. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae033. eCollection 2024 Apr. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 38525246 Free PMC article.
-
The ROCK-ezrin signaling pathway mediates LPS-induced cytokine production in pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 May 12;20(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00879-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 35551614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adderley S. P., Lawrence C., Madonia E., Olubadewo J. O., Breslin J. W. (2015). Histamine activates p38 MAP kinase and alters local lamellipodia dynamics, reducing endothelial barrier integrity and eliciting central movement of actin fibers. Am. J. Physiology-Cell Physiol. 309 (1), C51–C59. 10.1152/ajpcell.00096.2015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adyshev D. M., Moldobaeva N. K., Elangovan V. R., Garcia J. G. N., Dudek S. M. (2011). Differential involvement of Ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins in sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced human pulmonary endothelial cell barrier enhancement. Cell Signal. 23 (12), 2086–2096. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.08.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

