Estimation of Health-Related Physical Fitness Using Multiple Linear Regression in Korean Adults: National Fitness Award 2015-2019
- PMID: 34054580
- PMCID: PMC8155701
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.668055
Estimation of Health-Related Physical Fitness Using Multiple Linear Regression in Korean Adults: National Fitness Award 2015-2019
Abstract
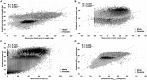
Continuous health care and the measurement of health-related physical fitness (HRPF) is necessary for prevention against chronic diseases; however, HRPF measurements including laboratory methods may not be practical for large populations owing to constraints such as time, cost, and the requirement for qualified technicians. This study aimed to develop a multiple linear regression model to estimate the HRPF of Korean adults, using easy-to-measure dependent variables, such as gender, age, body mass index, and percent body fat. The National Fitness Award datasets of South Korea were used in this analysis. The participants were aged 19-64 years, including 319,643 male and 147,600 females. HRPF included hand grip strength (HGS), flexibility (sit and reach), muscular endurance (sit-ups), and cardiorespiratory fitness (estimated VO2max ). An estimation multiple linear regression model was developed using the stepwise technique. The outlier data in the multiple regression model was identified and removed when the absolute value of the studentized residual was ≥2. In the regression model, the coefficient of determination for HGS (adjusted R 2: 0.870, P < 0.001), muscular endurance (adjusted R 2: 0.751, P < 0.001), and cardiorespiratory fitness (adjusted R 2: 0.885, P < 0.001) were significantly high. However, the coefficient of determination for flexibility was low (adjusted R 2: 0.298, P < 0.001). Our findings suggest that easy-to-measure dependent variables can predict HGS, muscular endurance, and cardiorespiratory fitness in adults. The prediction equation will allow coaches, athletes, healthcare professionals, researchers, and the general public to better estimate the expected HRPF.
Keywords: cardiorespiratory fitness; hand grip strength; health-related physical fitness; multiple linear regression; muscular endurance.
Copyright © 2021 Kim, Park, Jung, Lee and Lim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alahmari K. A., Silvian S. P., Reddy R. S., Kakaraparthi V. N., Ahmad I., Alam M. M. (2017). Hand grip strength determination for healthy males in Saudi Arabia: a study of the relationship with age, body mass index, hand length and forearm circumference using a hand-held dynamometer. J. Int. Med. Res. 45 540–548. 10.1177/0300060516688976 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bäckman E., Johansson V., Häger B., Sjöblom P., Henriksson K. G. (1995). Isometric muscle strength and muscular endurance in normal persons aged between 17 and 70 years. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 27 109–117. - PubMed
-
- Bardsiri V. K., Jawawi D. N. A., Hashim S. Z. M., Khatibi E. (2014). A flexible method to estimate the software development effort based on the classification of projects and localization of comparisons. Empiric. Softw. Eng. 19 857–884. 10.1007/s10664-013-9241-4 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources