OXA-484, an OXA-48-Type Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Class D β-Lactamase From Escherichia coli
- PMID: 34054758
- PMCID: PMC8153228
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.660094
OXA-484, an OXA-48-Type Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Class D β-Lactamase From Escherichia coli
Abstract
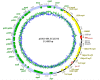
OXA-48-like carbapenemases are among the most frequent carbapenemases in Gram-negative Enterobacterales worldwide with the highest prevalence in the Middle East, North Africa and Europe. Here, we investigated the so far uncharacterized carbapenemase OXA-484 from a clinical E. coli isolate belonging to the high-risk clone ST410 regarding antibiotic resistance pattern, horizontal gene transfer (HGT) and genetic support. OXA-484 differs by the amino acid substitution 214G compared to the most closely related variants OXA-181 (214R) and OXA-232 (214S). The bla OXA - 484 was carried on a self-transmissible 51.5 kb IncX3 plasmid (pOXA-484) showing high sequence similarity with plasmids harboring bla OXA - 181. Intraspecies and intergenus HGT of pOXA-484 to different recipients occurred at low frequencies of 1.4 × 10-7 to 2.1 × 10-6. OXA-484 increased MICs of temocillin and carbapenems similar to OXA-232 and OXA-244, but lower compared with OXA-48 and OXA-181. Hence, OXA-484 combines properties of OXA-181-like plasmid support and transferability as well as β-lactamase activity of OXA-232.
Keywords: Enterobacterales; IncX; OXA-48; OXA-484; beta-lactamases; carbapenemases; plasmid.
Copyright © 2021 Sommer, Gerbracht, Krause, Wild, Tietgen, Riedel-Christ, Sattler, Hamprecht, Kempf and Göttig.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Choi K.-H. H., Kumar A., Schweizer H. P. (2006). A 10-min method for preparation of highly electrocompetent Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells: application for DNA fragment transfer between chromosomes and plasmid transformation. J. Microbiol. Methods 64 391–397. 10.1016/J.MIMET.2005.06.001 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

