The Antibody Receptor Fc Gamma Receptor IIIb Induces Calcium Entry via Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 2 in Human Neutrophils
- PMID: 34054821
- PMCID: PMC8155622
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.657393
The Antibody Receptor Fc Gamma Receptor IIIb Induces Calcium Entry via Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 2 in Human Neutrophils
Abstract
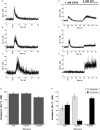
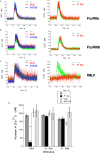
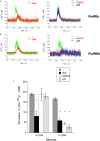
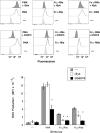
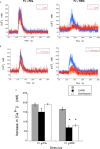
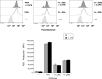
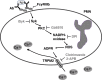
Human neutrophils express two unique antibody receptors for IgG, the FcγRIIa and the FcγRIIIb. FcγRIIa contains an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) sequence within its cytoplasmic tail, which is important for initiating signaling. In contrast, FcγRIIIb is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked receptor with no cytoplasmic tail. Although, the initial signaling mechanism for FcγRIIIb remains unknown, it is clear that both receptors are capable of initiating distinct neutrophil cellular functions. For example, FcγRIIa is known to induce an increase in L-selectin expression and efficient phagocytosis, while FcγRIIIb does not promote these responses. In contrast, FcγRIIIb has been reported to induce actin polymerization, activation of β1 integrins, and formation of neutrophils extracellular traps (NET) much more efficiently than FcγRIIa. Another function where these receptors seem to act differently is the increase of cytoplasmic calcium concentration. It has been known for a long time that FcγRIIa induces production of inositol triphosphate (IP3) to release calcium from intracellular stores, while FcγRIIIb does not use this phospholipid. Thus, the mechanism for FcγRIIIb-mediated calcium rise remains unknown. Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 2 (TRPM2) is a calcium permeable channel expressed in many cell types including vascular smooth cells, endothelial cells and leukocytes. TRPM2 can be activated by protein kinase C (PKC) and by oxidative stress. Because we previously found that FcγRIIIb stimulation leading to NET formation involves PKC activation and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, in this report we explored whether TRPM2 is activated via FcγRIIIb and mediates calcium rise in human neutrophils. Calcium rise was monitored after Fcγ receptors were stimulated by specific monoclonal antibodies in Fura-2-loaded neutrophils. The bacterial peptide fMLF and FcγRIIa induced a calcium rise coming initially from internal pools. In contrast, FcγRIIIb caused a calcium rise by inducing calcium entry from the extracellular medium. In addition, in the presence of 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) or of clotrimazole, two inhibitors of TRPM2, FcγRIIIb-induced calcium rise was blocked. fMLF- or FcγRIIa-induced calcium rise was not affected by these inhibitors. These data suggest for the first time that FcγRIIIb aggregation activates TRPM2, to induce an increase in cytoplasmic calcium concentration through calcium internalization in human neutrophils.
Keywords: Fc gamma receptor; PKC (protein kinase C); TRPM2 cation channel; calcium; neutrophil; reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2021 Alemán, Mora and Rosales.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fc gamma receptors activate different protein kinase C isoforms in human neutrophils.J Leukoc Biol. 2025 Apr 23;117(4):qiaf019. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiaf019. J Leukoc Biol. 2025. PMID: 39946245
-
Convergence of Fc gamma receptor IIA and Fc gamma receptor IIIB signaling pathways in human neutrophils.J Immunol. 2000 Jan 1;164(1):350-60. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.1.350. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10605030
-
FcgammaRIIA and FcgammaRIIIB mediate nuclear factor activation through separate signaling pathways in human neutrophils.J Immunol. 2009 Apr 15;182(8):4547-56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0801468. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19342628
-
Human neutrophil Fc gamma receptors: different buttons for different responses.J Leukoc Biol. 2023 Nov 24;114(6):571-584. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiad080. J Leukoc Biol. 2023. PMID: 37437115 Review.
-
Pathogenic effects of anti-Fc gamma receptor IIIb (CD16) on polymorphonuclear neutrophils in non-organ-specific autoimmune diseases.Autoimmun Rev. 2002 Feb;1(1-2):13-9. doi: 10.1016/s1568-9972(01)00002-7. Autoimmun Rev. 2002. PMID: 12849053 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell atlas of human gingiva unveils a NETs-related neutrophil subpopulation regulating periodontal immunity.J Adv Res. 2025 Jun;72:287-301. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.07.028. Epub 2024 Jul 30. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 39084404 Free PMC article.
-
The transient receptor potential channels in rheumatoid arthritis: Need to pay more attention.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 1;14:1127277. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1127277. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36926330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current development of Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs) in diagnostics: a review.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Aug 27;51(1):937. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09877-9. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39190190 Review.
-
Antibody-mediated control mechanisms of viral infections.Immunol Rev. 2024 Nov;328(1):205-220. doi: 10.1111/imr.13383. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Immunol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39162394 Review.
-
Phagosomal granulocytic ROS in septic patients induce the bacterial SOS response.iScience. 2024 Apr 26;27(6):109825. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109825. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38799552 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

