Antigen-Specific Regulatory T Cell Therapy in Autoimmune Diseases and Transplantation
- PMID: 34054826
- PMCID: PMC8160309
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.661875
Antigen-Specific Regulatory T Cell Therapy in Autoimmune Diseases and Transplantation
Abstract
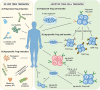
Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a heterogenous population of immunosuppressive T cells whose therapeutic potential for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and graft rejection is currently being explored. While clinical trial results thus far support the safety and efficacy of adoptive therapies using polyclonal Treg cells, some studies suggest that antigen-specific Treg cells are more potent in regulating and improving immune tolerance in a disease-specific manner. Hence, several approaches to generate and/or expand antigen-specific Treg cells in vitro or in vivo are currently under investigation. However, antigen-specific Treg cell therapies face additional challenges that require further consideration, including the identification of disease-relevant antigens as well as the in vivo stability and migratory behavior of Treg cells following transfer. In this review, we discuss these approaches and the potential limitations and describe prospective strategies to enhance the efficacy of antigen-specific Treg cell treatments in autoimmunity and transplantation.
Keywords: Tregs; antigen-specific Tregs; autoimmune disease (AD); regulatory T cells; therapy; transplantation.
Copyright © 2021 Selck and Dominguez-Villar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Coombes JL, Siddiqui KR, Arancibia-Carcamo CV, Hall J, Sun CM, Belkaid Y, et al. A Functionally Specialized Population of Mucosal CD103+ Dcs Induces Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells Via a TGF-beta and Retinoic Acid-Dependent Mechanism. J Exp Med (2007) 204:1757–64. 10.1084/jem.20070590 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

