Modifications of the BAFF/BAFF-Receptor Axis in Patients With Pemphigus Treated With Rituximab Versus Standard Corticosteroid Regimen
- PMID: 34054835
- PMCID: PMC8160507
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.666022
Modifications of the BAFF/BAFF-Receptor Axis in Patients With Pemphigus Treated With Rituximab Versus Standard Corticosteroid Regimen
Abstract
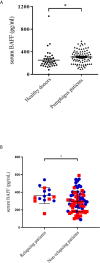
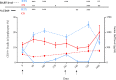
The efficacy of the B-cell-depleting agent rituximab has been reported in immune diseases but relapses are frequent, suggesting the need for repeated infusions. The B-cell activating factor (BAFF) is an important factor for B cell survival, class switch recombination and selection of autoreactive B cells, as well as maintaining long-lived plasma cells. It has been hypothesized that relapses after rituximab might be due to the increase of serum BAFF levels. From the Ritux3 trial, we showed that baseline serum BAFF levels were higher in pemphigus patients than in healthy donors (308 ± 13 pg/mL versus 252 ± 28 pg/mL, p=0.037) and in patients with early relapse compared who didn't (368 ± 92 vs 297 ± 118 pg/mL, p=0.036). Rituximab and high doses of CS alone have different effects on the BAFF/BAFF-R axis. Rituximab led to an increase of BAFF levels associated to a decreased mRNA (Day 0: 12.3 ± 7.6 AU vs Month 36: 3.3 ± 4.3 AU, p=0.01) and mean fluorescence intensity of BAFF-R in non-autoreactive (Day 0: 3232 vs Month 36: 1527, mean difference: 1705, 95%CI: 624 to 2786; p=0.002) as well as on reappearing autoreactive DSG-specific B cells (Day 0: 3873 vs Month 36: 2688, mean difference: 1185, 95%CI: -380 to 2750; p=0.20). Starting high doses of corticosteroids allowed a transitory decrease of serum BAFF levels that re-increased after doses tapering whereas it did not modify BAFF-R expression in autoreactive and non-autoreactive B cells. Our results suggest that the activation of autoreactive B cells at the onset of pemphigus is likely to be related to the presence of high BAFF serum levels and that the decreased BAFF-R expression after rituximab might be responsible for the delayed generation of memory B cells, resulting in a rather long period of mild pemphigus activity after rituximab therapy. Conversely, the incomplete B cell depletion and persistent BAFF-R expression associated with high BAFF serum levels might explain the high number of relapses in patients treated with CS alone.
Keywords: BAFF - B-cell activating factor; BAFF-receptor; Corticosteroïd; Pemphigus; rituximab.
Copyright © 2021 Hébert, Maho-Vaillant, Golinski, Petit, Riou, Boyer, Musette, Calbo and Joly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hebert V, Boulard C, Houivet E, Duvert Lehembre S, Borradori L, Della Torre R, et al. Large International Validation of ABSIS and PDAI Pemphigus Severity Scores. J Invest Dermatol (2018) 139(1):31–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

