RDUR, a lncRNA, Promotes Innate Antiviral Responses and Provides Feedback Control of NF-κB Activation
- PMID: 34054851
- PMCID: PMC8160526
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.672165
RDUR, a lncRNA, Promotes Innate Antiviral Responses and Provides Feedback Control of NF-κB Activation
Abstract
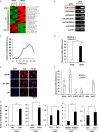
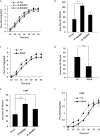
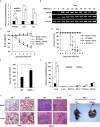
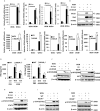
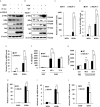
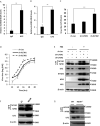
Influenza A virus (IAV), a highly infectious respiratory pathogen, remains a major threat to global public health. Numerous long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been shown to be implicated in various cellular processes. Here, we identified a new lncRNA termed RIG-I-dependent IAV-upregulated noncoding RNA (RDUR), which was induced by infections with IAV and several other viruses. Both in vitro and in vivo studies revealed that robust expression of host RDUR induced by IAV was dependent on the RIG-I/NF-κB pathway. Overexpression of RDUR suppressed IAV replication and downregulation of RDUR promoted the virus replication. Deficiency of mouse RDUR increased virus production in lungs, body weight loss, acute organ damage and consequently reduced survival rates of mice, in response to IAV infection. RDUR impaired the viral replication by upregulating the expression of several vital antiviral molecules including interferons (IFNs) and interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs). Further study showed that RDUR interacted with ILF2 and ILF3 that were required for the efficient expression of some ISGs such as IFITM3 and MX1. On the other hand, we found that while NF-κB positively regulated the expression of RDUR, increased expression of RDUR, in turn, inactivated NF-κB through a negative feedback mechanism to suppress excessive inflammatory response to viral infection. Together, the results demonstrate that RDUR is an important lncRNA acting as a critical regulator of innate immunity against the viral infection.
Keywords: NF-κB; inflammation; influenza A virus; innate immunity; long non-coding RNA.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Hu, Liu, Chen, Xiao, Li, Liao, Rai, Zhao, Ouyang, Pan, Zhang, Huang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of lncRNA-155 encoded by MIR155HG as a novel regulator of innate immunity against influenza A virus infection.Cell Microbiol. 2019 Aug;21(8):e13036. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13036. Epub 2019 May 29. Cell Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31045320
-
Long Noncoding RNA IFITM4P Regulates Host Antiviral Responses by Acting as a Competing Endogenous RNA.J Virol. 2021 Oct 13;95(21):e0027721. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00277-21. Epub 2021 Jul 21. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34287042 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP2 Suppresses Host Innate Immunity against Influenza A Virus by Regulating EGFR-Mediated Signaling.J Virol. 2021 Feb 24;95(6):e02001-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02001-20. Print 2021 Feb 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33361428 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Host Non-Coding RNAs in the Pathogenesis of the Influenza Virus.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 27;18(1):39. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010039. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 28035991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate Immune Sensing of Influenza A Virus.Viruses. 2020 Jul 14;12(7):755. doi: 10.3390/v12070755. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32674269 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The lncRNAs involved in regulating the RIG-I signaling pathway.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Nov 9;12:1041682. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1041682. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36439216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a Novel lncRNA LNC_001186 and Its Effects on CPB2 Toxin-Induced Apoptosis of IPEC-J2 Cells.Genes (Basel). 2023 May 6;14(5):1047. doi: 10.3390/genes14051047. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239407 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Hidden Regulators: The Impact of lncRNAs on Zoonoses.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 21;25(6):3539. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063539. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome-wide 5-methylcytosine modification profiling of long non-coding RNAs in A549 cells infected with H1N1 influenza A virus.BMC Genomics. 2023 Jun 12;24(1):316. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09432-z. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37308824 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Involvement of Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription in the Pathogenesis of Influenza A Virus.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 19;25(24):13589. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413589. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769350 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

