Development, Identification, and Application of a Germplasm Specific SCAR Marker for Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo
- PMID: 34054907
- PMCID: PMC8160518
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.669458
Development, Identification, and Application of a Germplasm Specific SCAR Marker for Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo
Abstract
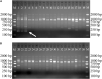
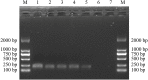
The stems of Dendrobium officinale have been used as a rare and valuable Chinese tonic medicine, known as "Tiepi Fengdou", since the Qing dynasty. Because of the increased market demand and continued exploitation of this plant, the reserves of wild D. officinale resources have been depleted, and D. officinale products on the market are being increasingly adulterated. Such changes have strongly affected the sustainable utilization of this valuable medicinal plant resource and the development of related industries. In this study, a species-specific DNA marker was developed for the rapid and accurate authentication of D. officinale. In total, 36 start codon-targeted (SCoT) polymorphism primers were screened in 36 definite Dendrobium species, and a distinct species-specific DNA amplicon (SCoT13-215) for D. officinale was obtained. After the sequence was cloned and sequenced, a sequence-characterized amplified region marker was developed (named SHF/SHR) and validated through PCR amplification of all 38 Dendrobium samples. The marker's specificity for D. officinale was confirmed through the consistent amplification of a clear 197-bp band. This SCAR marker can be used to rapidly, effectively, and reliably identify D. officinale among various Dendrobium species and may play an important role in ensuring the quality of medicinal preparations and protecting the germplasm of this important medicinal species.
Keywords: DNA markers; Dendrobium officinale; SCAR marker; SCoT; species identification.
Copyright © 2021 Zheng, Cai, Chen, Gao, Jin, Wang, Feng and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
SNP, ARMS and SSH authentication of medicinal Dendrobium officinale KIMURA et MIGO and application for identification of Fengdou drugs.Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Apr;31(4):553-7. doi: 10.1248/bpb.31.553. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008. PMID: 18379039
-
Rapid identification of Dendrobium officinale using Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) method.Chin J Nat Med. 2019 May 20;17(5):337-345. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(19)30039-1. Chin J Nat Med. 2019. PMID: 31171268
-
Analysis of the Dendrobium officinale transcriptome reveals putative alkaloid biosynthetic genes and genetic markers.Gene. 2013 Sep 15;527(1):131-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.05.073. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23756193
-
Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo: A Review on Its Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Industrialization.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:7436259. doi: 10.1155/2017/7436259. Epub 2017 Mar 12. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28386292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Advances in Multi-Omics on the Traditional Chinese Herb Dendrobium officinale.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jan 11;12:808228. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.808228. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35087561 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid Diagnostic PCR Assay Method for Species Identification of Mantidis Ootheca (Sangpiaoxiao) Based on Cytochrom C Oxidase I (COI) Barcode Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 23;25(18):10224. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810224. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337711 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Family and Functional Analysis of DcAP2/ERF#96 Associated with Abiotic Stress in Dendrobium catenatum.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 6;23(21):13603. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113603. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362389 Free PMC article.
-
Development of SCAR Markers for Genetic Authentication of Metarhizium acridum.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Apr 4;10(4):269. doi: 10.3390/jof10040269. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667940 Free PMC article.
-
Development of species-specific ISSR-derived SCAR marker for early discrimination between Cinnamomum verum and Cinnamomum cassia.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Aug;50(8):6311-6321. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08578-z. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37306873
-
Development and Application of a Cultivar-Specific Sequence-Characterized Amplified Region (SCAR) Marker for the Detection of Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. 'Daboju'.Plants (Basel). 2022 Feb 24;11(5):604. doi: 10.3390/plants11050604. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35270074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collard B. C. Y., Mackill D. J. (2009). Start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism: a simple, novel DNA marker technique for generating gene-targeted markers in plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 27 86–93. 10.1007/s11105-008-0060-5 - DOI
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission (2015). Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 2015 Edn, Vol. part I. Beijing: China medical science and technology press, 282.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

