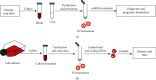
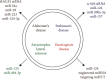
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Potential of Exosomal MicroRNAs for Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 34054944
- PMCID: PMC8143892
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8884642
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Potential of Exosomal MicroRNAs for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
Neurodegenerative disorders (NDs) are characterized by a gradual loss of neurons and functions that eventually leads to progressive neurological impairment. In view of the heavy burden on the healthcare system, efficient and reliable biomarkers for early diagnosis and therapeutic treatments to reverse the progression of NDs are in urgent need. There has been an increasing interest in using exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers or targeted therapies for neurological diseases recently. In this review, we overviewed the updated studies on exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers and potential therapeutic approaches in NDs, as well as their association with the pathophysiology of this group of disorders, especially Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and Huntington's disease (HD). The exosomal miRNAs that are commonly dysregulated across different NDs or are commonly used as therapeutic candidates were also identified and summarized. In summary, the feasibility of exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers and potential targeted therapy for NDs has been verified. However, due to the limitations of existing studies and the discrepancies across different studies, high quality laboratory and clinical investigations are still required.
Copyright © 2021 Miao He et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosomal microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases.Neurol Res. 2023 Mar;45(3):191-199. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2022.2129768. Epub 2022 Oct 2. Neurol Res. 2023. PMID: 36184105 Review.
-
MicroRNA Alteration, Application as Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Approaches in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 25;23(9):4718. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094718. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Dysregulated microRNA Biogenesis Machinery and microRNA Sorting on Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 8;24(4):3443. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043443. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Biomarkers and Their Implications for the Early Diagnosis of Selected Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 21;23(9):4610. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094610. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating brain-enriched microRNAs as novel biomarkers for detection and differentiation of neurodegenerative diseases.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2017 Nov 9;9(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s13195-017-0316-0. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29121998 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Huntingtin Co-Isolates with Small Extracellular Vesicles from Blood Plasma of TgHD and KI-HD Pig Models of Huntington's Disease and Human Blood Plasma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 17;23(10):5598. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105598. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628406 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of age and sex on microRNA response and recovery in the hippocampus following sepsis.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Jan 30;14(2):728-746. doi: 10.18632/aging.203868. Epub 2022 Jan 30. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35094981 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes in Regulating miRNAs for Biomarkers of Neurodegenerative Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun;62(6):7576-7596. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04733-8. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39918711 Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicular miRNA in Pancreatic Cancer: From Lab to Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 8;16(12):2179. doi: 10.3390/cancers16122179. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNAs as Predictive Biomarkers in Postoperative Delirium After Spine Surgery: Preliminary Study.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024 Nov 1;79(11):glae162. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glae162. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38970345 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous