Prognostic Impact of Ki-67 Change in Locally Advanced and Early Breast Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Single Institution Experience
- PMID: 34054952
- PMCID: PMC8112947
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5548252
Prognostic Impact of Ki-67 Change in Locally Advanced and Early Breast Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Single Institution Experience
Abstract
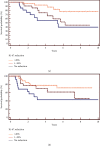
Systemic neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NCT) is a standard treatment for locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) and for selected early breast cancer (EBC). In these settings, the prognostic and predictive role of Ki-67 before and after NCT is unclear. The aim of our study was to investigate the prognostic role of Ki-67 change in patients not achieving pathological complete response (pCR). We retrospectively analyzed data of patients who did not achieve pCR assessing Ki-67 expression pre- and post-NCT. We stratified three groups: high reduction (>20%), low reduction (1-20%), and no reduction in Ki-67. These groups were correlated with clinical and pathological data by χ2 test. We estimated disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) using Kaplan-Meier method, and we adopted univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard models. We selected 82 patients from a database of 143 patients, excluding those who were metastatic at diagnosis, achieved pCR, or lack data regarding Ki-67. Median age at diagnosis was 54 years (range 30-75); 51 patients were Luminal B, 10 human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2) enriched, and 21 triple negative. A significant correlation between high Ki-67 reduction and luminal B HER-2-negative subtype was observed (p = 0,0035). The change in Ki-67 was significantly associated with DFS (p = 0,0596) and OS (p = 0,0120), also at multivariate analysis (p = 0,0256 for DFS; p = 0,0093 for OS). In particular, as compared to patients with low/no reduction of Ki-67, those with high Ki-67 reduction (>20%) after NCT showed better survival (60% vs. 56% vs. 83% after 5 years from diagnosis, respectively; p = 0.01). In conclusion, in our study, Ki-67 change showed a significant prognostic role in breast cancer patients treated with NCT who did not achieve pCR. Crucially, Ki-67 < 20% identifies a high-risk population that may be eligible for clinical trials with novel therapeutic interventions in adjuvant setting.
Copyright © 2021 Mirco Pistelli et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Different prognostic significance of Ki-67 change between pre- and post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various subtypes of breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Jan;137(1):203-12. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2344-6. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 23184081
-
Progesterone receptor loss identifies luminal-type local advanced breast cancer with poor survival in patients who fail to achieve a pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy.Oncotarget. 2015 Jul 20;6(20):18174-82. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4225. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26053183 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of ER, PgR, HER-2, Ki-67, cyclin D1, and nm23-H1 as predictors of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced breast cancer.Med Oncol. 2011 Dec;28 Suppl 1:S31-8. doi: 10.1007/s12032-010-9676-z. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Med Oncol. 2011. PMID: 20844986
-
Progesterone Receptors, Pathological Complete Response and Early Outcome for Locally Advanced Breast Cancer - a Single Centre Study. (PPLB - 01).Indian J Surg Oncol. 2016 Dec;7(4):397-406. doi: 10.1007/s13193-016-0523-3. Epub 2016 Apr 23. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27872526 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in patients with breast cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;608:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-74039-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17993229 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic analysis of three forms of Ki-67 in patients with breast cancer with non-pathological complete response before and after neoadjuvant systemic treatment.Cancer Med. 2023 Apr;12(8):9363-9372. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5693. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36794698 Free PMC article.
-
Pre- and Post-Neoadjuvant Clinicopathological Parameters Can Help in the Prognosis and the Prediction of Response in HER2+ and Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 6;15(12):3068. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123068. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370679 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant docetaxel and capecitabine (TX) versus docetaxel and epirubicin (TE) for locally advanced or early her2-negative breast cancer: an open-label, randomized, multi-center, phase II Trial.BMC Cancer. 2022 Dec 28;22(1):1357. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10439-0. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36577958 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Biomarker Dynamics and Long-Term Treatment Outcomes in Breast Cancer Patients with Residual Cancer Burden after Neoadjuvant Therapy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jul 18;12(7):1740. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12071740. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35885644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nishimura R., Osako T., Okomura Y., Hayashi M., Toyozumi Y., Arimal N. Ki-67 as a prognostic marker according to breast cancer subtype and a predictor of recurrence time in primary breast cancer. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 2010;1(5):747–754. doi: 10.3892/etm.2010.133. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous