A Systematic Review of Antiaging Effects of 23 Traditional Chinese Medicines
- PMID: 34055012
- PMCID: PMC8143881
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5591573
A Systematic Review of Antiaging Effects of 23 Traditional Chinese Medicines
Abstract
Background: Aging is an inevitable stage of body development. At the same time, aging is a major cause of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative diseases. Chinese herbal medicine is a natural substance that can effectively delay aging and is expected to be developed as antiaging drugs in the future. Aim of the review. This paper reviews the antiaging effects of 23 traditional Chinese herbal medicines or their active components. Materials and methods. We reviewed the literature published in the last five years on Chinese herbal medicines or their active ingredients and their antiaging role obtained through the following databases: PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, and Web of Science.
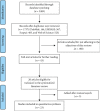
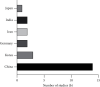
Results: A total of 2485 papers were found, and 212 papers were screened after removing the duplicates and reading the titles. Twenty-three studies met the requirements of this review and were included. Among these studies, 13 articles used Caenorhabditis elegans as the animal model, and 10 articles used other animal models or cell lines.
Conclusion: Chinese herbal medicines or their active components play an antiaging role by regulating genes related to aging through a variety of signaling pathways. Chinese herbal medicines are expected to be developed as antiaging drugs or used in the medical cosmetology industry.
Copyright © 2021 Lixin Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
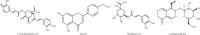


References
-
- Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures, Alzheimer’s & dementia. The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association. 2016;12(4):459–509. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

