Therapeutic Effects of Traditional Chinese Exercises on Musculoskeletal Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34055119
- PMCID: PMC8131159
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5584997
Therapeutic Effects of Traditional Chinese Exercises on Musculoskeletal Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: The number of patients with musculoskeletal pain, which seriously affects people's quality of life, has increased. Traditional Chinese exercises are accepted and practiced to strengthen the body.
Objective: This study aims to explore the efficacy of traditional Chinese exercises for the treatment of musculoskeletal pain.
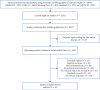
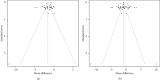
Methods: A comprehensive search of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) related to traditional Chinese exercises on patients with musculoskeletal pain was completed using PubMed, SinoMed, CNKI, VIP, and Wanfang Med Online databases. All RCTs published until February 2021 were considered. Two researchers independently screened the literature according to the predesigned inclusion and exclusion criteria, and data was extracted and assessed for their risk of bias via the Cochrane collaboration tool. Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan5.2 and Rx64 4.0.2 software.
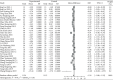
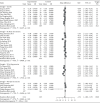
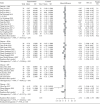
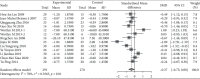
Results: A total of 45 RCT studies with 3178 patients were included. Traditional Chinese exercises were able to effectively alleviate patients with musculoskeletal pain (MD = -1.54, 95% confidence interval (-1.88, -1.19), P < 0.01). Among them, the Yi Jin Jing exercise was superior to other exercises, while Wu Qin Xi showed no significant effects. Besides, traditional Chinese exercises had significant positive effects on the dysfunction and stiffness of the waist and knee joints. Traditional Chinese exercises could effectively relieve the clinical symptoms of patients with musculoskeletal pain. Particularly, the Yi Jin Jing exercise presented the most significant positive effect on pain reduction.
Copyright © 2021 Zhenrui Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of traditional Chinese exercise in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Int J Rheum Dis. 2023 Dec;26(12):2380-2389. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14924. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Int J Rheum Dis. 2023. PMID: 37813823
-
Comparative effects of Yi Jin Jing versus Tai Chi exercise training on benign prostatic hyperplasia-related outcomes in older adults: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2016 Jul 16;17(1):319. doi: 10.1186/s13063-016-1448-4. Trials. 2016. PMID: 27422168 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of traditional Chinese exercises in fibromyalgia syndrome: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Complement Ther Med. 2024 Mar;80:103019. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2024.103019. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Complement Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 38211633 Review.
-
The Beneficial Effect of Traditional Chinese Exercises on the Management of Obesity.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Oct 1;2020:2321679. doi: 10.1155/2020/2321679. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33062003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Wu Qin Xi exercises on pain and function in people with knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 7;9:979207. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.979207. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36419784 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Applications and Prescriptions of Motion Style Acupuncture Treatment for Musculoskeletal Pain: A Scoping Review of Clinical Controlled Trials.J Pain Res. 2025 Jun 28;18:3275-3287. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S529676. eCollection 2025. J Pain Res. 2025. PMID: 40613071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of non-pharmacological therapy under the guidance of TCM theory in the treatment of anxiety in patients with myocardial infarction: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 6;18(7):e0288154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288154. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37410737 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Traditional Chinese Exercise Yijinjing on Disability and Muscle Strength Among Patients With Chronic Low Back Pain: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2025 May 7;14:e67557. doi: 10.2196/67557. JMIR Res Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40334269 Free PMC article.
-
Commentary: Current Evidence on Traditional Chinese Exercises for Quality of Life in Patients With Essential Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jan 5;8:801392. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.801392. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35071365 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Traditional Chinese Exercises on Pain and Disability in Middle-Aged and Elderly Patients With Neck Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Jun 10;14:912945. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.912945. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35754953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu E., Li S. S., Wu C. W., et al. Factors influencing the prevalence of anxiety and depression in patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain. World Latest Medicne Information (Electronic Version) 2019;19(45):114–116.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

