Meta-analysis of peptides to detect protein significance
- PMID: 34055134
- PMCID: PMC8162183
- DOI: 10.4310/sii.2020.v13.n4.a4
Meta-analysis of peptides to detect protein significance
Abstract
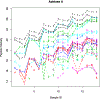
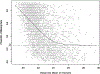
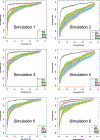
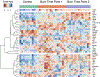
Shotgun assays are widely used in biotechnologies to characterize large molecules, which are hard to be measured as a whole directly. For instance, in Liquid Chromatography - Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) shotgun experiments, proteins in biological samples are digested into peptides, and then peptides are separated and measured. However, in proteomics study, investigators are usually interested in the performance of the whole proteins instead of those peptide fragments. In light of meta-analysis, we propose an adaptive thresholding method to select informative peptides, and combine peptide-level models to protein-level analysis. The meta-analysis procedure and modeling rationale can be adapted to data analysis of other types of shotgun assays.
Keywords: Adaptive thresholding; Meta-analysis; Shotgun technology.
Figures
References
-
- Aebersold R and Mann M (2003). Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature 422 198–207. - PubMed
-
- Belczacka I, Latosinska A, Metzger J, Marx D, Vlahou A, Mischak H and Frantzi M (2019). Proteomics biomarkers for solid tumors: Current status and future prospects. Mass spectrometry reviews 38 49–78. - PubMed
-
- Bellew M, Coram M, Fitzgibbon M, Igra M, Randolph T, Wang P, May D, Eng J, Fang R, Lin C, Chen J, Goodlett D, Whiteaker J, Paulovich A and McIntosh M (2006). A suite of algorithms for the comprehensive analysis of complex protein mixtures using high-resolution LC-MS. Bioinformatics 22 1902–9. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum A (1954). Combining independent tests of significance. Journal of the American Statistical Association 559–74. MR0065101
-
- Clough T, Key M, Ott I, Ragg S, Schadow G and Vitek O (2009). Protein quantification in label-free LC-MS experiments. Journal of proteome research 8 5275–84. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
