Limited correlation between tumor markers and minimal residual disease detected by seven neuroblastoma-associated mRNAs in high-risk neuroblastoma patients
- PMID: 34055352
- PMCID: PMC8145602
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2021.2299
Limited correlation between tumor markers and minimal residual disease detected by seven neuroblastoma-associated mRNAs in high-risk neuroblastoma patients
Abstract
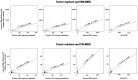
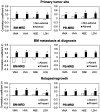
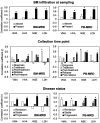
Vanillylmandelic acid (VMA), homovanillic acid (HVA), neuron-specific enolase (NSE) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) are classical tumor markers and are used as standard clinical evaluations for patients with neuroblastoma (NB). Minimal residual disease (MRD) can be monitored by quantifying several sets of NB-associated mRNAs in the bone marrow (BM) and peripheral blood (PB) of patients with NB. Although MRD in BM and PB has been revealed to be a strong prognostic factor that is independent of standard clinical evaluations, its interrelation with tumor markers remains uncharacterized. The present study determined the levels of tumor markers (VMA, HVA, NSE and LDH) and MRD (BM-MRD and PB-MRD) in 133 pairs of concurrently collected BM, PB and urine samples from 19 patients with high-risk NB. The patients were evaluated during the entire course of treatment, which included 10 diagnoses, 32 treatments, 36 post-treatment, 9 relapses and 46 post-relapse sample pairs. The level of BM-MRD and PB-MRD was determined by quantifying 7 NB-mRNAs (collapsin response mediator protein 1, dopamine beta-hydroxylase, dopa decarboxylase, growth-associated protein 43, ISL LIM homeobox 1, pairedlike homeobox 2b and tyrosine hydroxylase) using droplet digital PCR. In overall sample pairs, tumor markers (VMA, HVA, NSE and LDH) demonstrated weak but significant correlations (P<0.011) with BM-MRD and PB-MRD. In subgroups according to each patient evaluation, the degree of correlation between tumor markers and MRD became stronger in patients with adrenal gland tumors, BM metastasis at diagnosis and relapse/regrowth compared with overall sample pairs. In contrast, tumor markers demonstrated variable correlations with MRD in subgroups according to each sample evaluation (BM infiltration at sampling, collection time point and disease status). The results suggested that tumor markers may demonstrate limited correlation with MRD in patients with high-risk NB.
Keywords: homovanillic acid; lactate dehydrogenase; minimal residual disease; neuroblastoma; neuroblastoma-associated mRNAs; neuron-specific enolase; tumor markers; vanillylmandelic acid.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
NNis received institutional research funding from Sysmex Corporation to Kobe University. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
