A Case of Hemodynamically Unstable Sick Sinus Syndrome Secondary to Refeeding Syndrome
- PMID: 34055503
- PMCID: PMC8148626
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14625
A Case of Hemodynamically Unstable Sick Sinus Syndrome Secondary to Refeeding Syndrome
Abstract
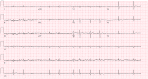
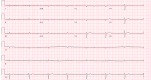
Prolonged malnourished states can predispose patients to refeeding syndrome with the uncommon complication of cardiogenic shock if not corrected initially. While refeeding syndrome is well studied its complications may not be easily identified in the setting of rapid deterioration. This case report reviews the events of a 57-year-old male who was brought in by law enforcement, for altered mental status and agitation, after being found wandering in the woods. The patient was initially hemodynamically stable but developed cardiogenic shock from sick sinus syndrome. The patient's shock was non-responsive to IV fluid resuscitation and required ICU admission. Congestive heart failure, ischemic cardiomyopathy, substance abuse, myocarditis, and endocarditis were considered but ruled out. Patient's symptoms improved after electrolyte repletion following brief ICU admission with dopamine drip.
Keywords: cardiac arrhythmia; cardiogenic shock; refeeding syndrome; sick sinus syndrome; tachy-brady syndrome.
Copyright © 2021, Mgerian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Dakkak W, Doukky R. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2020. Sick Sinus Syndrome. - PubMed
-
- The pathophysiology and clinical characteristics of severe hypophosphatemia. Knochel JP. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/836118/ Arch Intern Med. 1977;137:203–220. - PubMed
-
- Functional roles of Na,K-ATPase subunits. Geering K. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2008;17:526–532. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources