Medical Community Perspectives Regarding the Egyptian Medical Licensing Exam: A Mixed-Method Study
- PMID: 34055507
- PMCID: PMC8148620
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14636
Medical Community Perspectives Regarding the Egyptian Medical Licensing Exam: A Mixed-Method Study
Abstract
Background: Although national licensing examinations (NLEs) may be a costly process, they can predict performance of medical practitioners for many years following graduation. The current licensing requirements do not fulfill this function as there are no clear performance criteria for them. Therefore, new requirements should be developed and announced.
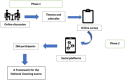
Objective: The study aims to develop a framework for the Egyptian Medical Licensing Exam (EMLE) by exploring the opinions and perceptions of Egyptian health practitioners and medical educators.
Methods: This study is a two-phase exploratory mixed-method study. An online discussion forum was conducted with medical practitioners and educators concerning the development of the EMLE. Then, an online survey was distributed to explore the opinions of medical practitioners and educators about the EMLE.
Results: Fifty medical practitioners and educators participated in the discussion forum about the development of the EMLE, while 266 participants responded to the online survey. The responses of the participants contributed to the development of a framework for the EMLE that is divided into two main sections, the exam logistics and the exam set up. The exam logistics included the exam committee, prerequisites for the exam, the admission criteria and fees, and validity of the license. The exam set up included exam setting, structure, pass marks, and exam retake policy.
Conclusion: The study concluded that medical practitioners and educators could contribute greatly to the planning for the EMLE. Their opinions are based on their experiences and include the timing of the exam, blueprinting, assessment methods, psychometrics and retake.
Keywords: egypt; emle framework; exam logistics; exam set up; national licensing exam.
Copyright © 2021, Abdel Nasser et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The International Landscape of Medical Licensing Examinations: A Typology Derived From a Systematic Review.Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018 Sep 1;7(9):782-790. doi: 10.15171/ijhpm.2018.32. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2018. PMID: 30316226 Free PMC article.
-
Perception survey on the introduction of clinical performance examination as part of the national nursing licensing examination in Korea.J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2017 Oct 25;14:26. doi: 10.3352/jeehp.2017.14.26. eCollection 2017. J Educ Eval Health Prof. 2017. PMID: 29129904 Free PMC article.
-
The Early Impact of Deciding to Take the United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 for Osteopathic Medical Students in the Pass/Fail Era.Cureus. 2023 Mar 14;15(3):e36154. doi: 10.7759/cureus.36154. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37065396 Free PMC article.
-
Are study strategies related to medical licensing exam performance?Int J Med Educ. 2014 Nov 2;5:199-204. doi: 10.5116/ijme.5439.6491. Int J Med Educ. 2014. PMID: 25362627 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring students' [pre-pandemic] use and the impact of commercial-off-the-shelf learning platforms on students' national licensing exam performance: A focused review - BEME Guide No. 72.Med Teach. 2022 Jul;44(7):707-719. doi: 10.1080/0142159X.2022.2039380. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Med Teach. 2022. PMID: 35271398 Review.
Cited by
-
A commentary on the National Medical Licensing Examination in Vietnam: why, what, who and how.MedEdPublish (2016). 2023 Sep 6;13:30. doi: 10.12688/mep.19654.2. eCollection 2023. MedEdPublish (2016). 2023. PMID: 37753390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The medical licensing examination debate. Archer J, Lynn N, Coombes L, Roberts M, Gale T, de Bere SR. Regul Gov. 2017;11:315–322.
-
- Trends in national licensing examinations in medicine. Swanson DB, Roberts TE. Med Educ. 2016;50:101–114. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources