Acute syndesmotic injuries in ankle fractures: From diagnosis to treatment and current concepts
- PMID: 34055585
- PMCID: PMC8152437
- DOI: 10.5312/wjo.v12.i5.270
Acute syndesmotic injuries in ankle fractures: From diagnosis to treatment and current concepts
Abstract
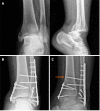
A stable and precise articulation of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis maintains the tibiofibular relationship, and it is essential for normal motion of the ankle joint. The disruption of this joint is frequently accompanied by rotational ankle fracture, such as pronation-external rotation, and rarely occurs without ankle fracture. The diagnosis is not simple, and ideal management of the various presentations of syndesmotic injury remains controversial to this day. Anatomical restoration and stabilization of the disrupted tibiofibular syndesmosis is essential to improve functional outcomes. In such an injury, including inadequately treated, misdiagnosed and correctly diagnosed cases, a chronic pattern characterized by persistent ankle pain, function disability and early osteoarthritis can result. This paper reviews anatomical and biomechanical characteristics of this syndesmosis, the mechanism of its acute injury associated to fractures, radiological and arthroscopic diagnosis and surgical treatment.
Keywords: Ankle; Distal tibiofibular joint; Fracture; Injury; Syndesmosis; Trauma.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interests for this article.
Figures

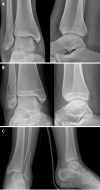
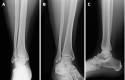


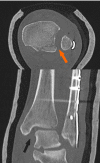

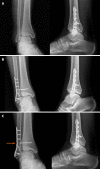


References
-
- Kocadal O, Yucel M, Pepe M, Aksahin E, Aktekin CN. Evaluation of Reduction Accuracy of Suture-Button and Screw Fixation Techniques for Syndesmotic Injuries. Foot Ankle Int . 2016;37:1317–1325. - PubMed
-
- Lubberts B, Guss D, Vopat BG, Johnson AH, van Dijk CN, Lee H, DiGiovanni CW. The arthroscopic syndesmotic assessment tool can differentiate between stable and unstable ankle syndesmoses. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc . 2020;28:193–201. - PubMed
-
- Gan K, Xu D, Hu K, Wu W, Shen Y. Dynamic fixation is superior in terms of clinical outcomes to static fixation in managing distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc . 2020;28:270–280. - PubMed
-
- Brosky T, Nyland J, Nitz A, Caborn DN. The ankle ligaments: consideration of syndesmotic injury and implications for rehabilitation. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther . 1995;21:197–205. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

