Chest computed tomography as a primary tool in COVID-19 detection: an update meta-analysis
- PMID: 34055674
- PMCID: PMC8149579
- DOI: 10.1007/s40336-021-00434-z
Chest computed tomography as a primary tool in COVID-19 detection: an update meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: A growing number of publications have paid close attention to the chest computed tomography (CT) detection of COVID-19 with inconsistent diagnostic accuracy, the present meta-analysis assessed the available evidence regarding the overall performance of chest CT for COVID-19.
Methods: 2 × 2 diagnostic table was extracted from each of the included studies. Data on specificity (SPE), sensitivity (SEN), negative likelihood ratio (LR-), positive likelihood ratio (LR+), and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) were calculated purposefully.
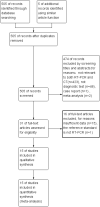
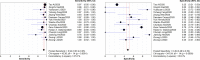
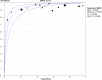
Results: Fifteen COVID-19 related publications met our inclusion criteria and were judged qualified for the meta-analysis. The following were summary estimates for diagnostic parameters of chest CT for COVID-19: SPE, 0.49 (95% CI 46-52%); SEN, 0.94 (95% CI 93-95%); LR-, 0.15 (95% CI 11-20%); LR+, 1.93 (95% CI 145-256%); DOR, 17.14 (95% CI 918-3199%); and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), 0.93.
Conclusion: Chest CT has high SEN, but the SPE is not ideal. It is highly recommended to use a combination of different diagnostic tools to achieve sufficient SEN and SPE. It should be taken into account as a diagnostic tool for current COVID-19 detection, especially for patients with symptoms.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s40336-021-00434-z.
Keywords: COVID-19 detection; Chest CT; Meta-analysis; RT-PCR.
© Italian Association of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diagnostic value of chest computed tomography imaging for COVID-19 based on reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction: a meta-analysis.Infect Dis Poverty. 2021 Oct 21;10(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s40249-021-00910-8. Infect Dis Poverty. 2021. PMID: 34674774 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT and 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT in primary liver cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Hell J Nucl Med. 2023 May-Aug;26(2):123-131. doi: 10.1967/s002449912575. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Hell J Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 37527048
-
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 30;9:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 26;11:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub3. PMID: 32997361 Updated.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of shear wave elastography for endometrial cancer: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jan 27;102(4):e32700. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032700. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36705368 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound superb microvascular imaging for breast tumor: a meta-analysis.Med Ultrason. 2020 Sep 5;22(3):313-318. doi: 10.11152/mu-2460. Med Ultrason. 2020. PMID: 32898204
Cited by
-
Auxiliary screening COVID-19 by computed tomography.Front Public Health. 2023 Jun 5;11:974542. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.974542. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37342278 Free PMC article.
-
Chest Computed Tomography Is an Efficient Method for Initial Diagnosis of COVID-19: An Observational Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 12;9:848656. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.848656. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35492320 Free PMC article.
-
Post-infectious ST elevation myocardial infarction following a COVID-19 infection: A case report.Biomed Rep. 2022 Feb;16(2):10. doi: 10.3892/br.2021.1493. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Biomed Rep. 2022. PMID: 34987794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- China National Health Commission (2020) 7th edition of the Diagnosis and Treatment Program of the 2019 New Coronavirus Pneumonia issued by the National Health Commission of China.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
