The Potential Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Liver Fibrosis Theranostics
- PMID: 34055744
- PMCID: PMC8161198
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.674786
The Potential Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Liver Fibrosis Theranostics
Abstract
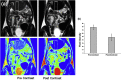
Liver fibrosis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide due to chronic liver damage and leading to cirrhosis, liver cancer, and liver failure. To date, there is no effective and specific therapy for patients with hepatic fibrosis. As a result of their various advantages such as biocompatibility, imaging contrast ability, improved tissue penetration, and superparamagnetic properties, magnetic nanoparticles have a great potential for diagnosis and therapy in various liver diseases including fibrosis. In this review, we focus on the molecular mechanisms and important factors for hepatic fibrosis and on potential magnetic nanoparticles-based therapeutics. New strategies for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis are also discussed, with a summary of the challenges and perspectives in the translational application of magnetic nanoparticles from bench to bedside.
Keywords: drug delivery; liver fibrosis; magnetic nanoparticles; nanomedicine; theranostics.
Copyright © 2021 Eftekhari, Arjmand, Asheghvatan, Švajdlenková, Šauša, Abiyev, Ahmadian, Smutok, Khalilov, Kavetskyy and Cucchiarini.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Armstrong M. J., Gaunt P., Aithal G. P., Barton D., Hull D., Parker R., et al. (2016). Liraglutide Safety and Efficacy in Patients with Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (LEAN): A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Study. Lancet 387 (10019), 679–690. 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00803-X - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

