A Microfluidic Hanging-Drop-Based Islet Perifusion System for Studying Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion From Multiple Individual Pancreatic Islets
- PMID: 34055765
- PMCID: PMC8149801
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.674431
A Microfluidic Hanging-Drop-Based Islet Perifusion System for Studying Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion From Multiple Individual Pancreatic Islets
Abstract
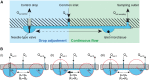
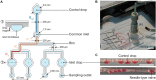
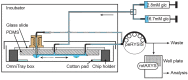
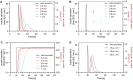
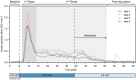
Islet perifusion systems can be used to monitor the highly dynamic insulin release of pancreatic islets in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) assays. Here, we present a new generation of the microfluidic hanging-drop-based islet perifusion platform that was developed to study the alterations in insulin secretion dynamics from single pancreatic islet microtissues at high temporal resolution. The platform was completely redesigned to increase experimental throughput and to reduce operational complexity. The experimental throughput was increased fourfold by implementing a network of interconnected hanging drops, which allows for performing GSIS assays with four individual islet microtissues in parallel with a sampling interval of 30 s. We introduced a self-regulating drop-height mechanism that enables continuous flow and maintains a constant liquid volume in the chip, which enables simple and robust operation. Upon glucose stimulation, reproducible biphasic insulin release was simultaneously observed from all islets in the system. The measured insulin concentrations showed low sample-to-sample variation as a consequence of precise liquid handling with stable drop volumes, equal flow rates in the channels, and accurately controlled sampling volumes in all four drops. The presented device will be a valuable tool in islet and diabetes research for studying dynamic insulin secretion from individual pancreatic islets.
Keywords: glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS); hanging drops; microfluidics; organ on chip; pancreatic islets; perifusion systems.
Copyright © 2021 Wu Jin, Rousset, Hierlemann and Misun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Birchler A., Berger M., Jäggin V., Lopes T., Etzrodt M., Misun P. M., et al. (2016). Seamless combination of fluorescence-activated cell sorting and hanging-drop networks for individual handling and culturing of stem cells and microtissue spheroids. Anal. Chem. 88 1222–1229. 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03513 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

