Differentiation and Application of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Derived Cardiovascular Cells for Treatment of Heart Diseases: Promises and Challenges
- PMID: 34055788
- PMCID: PMC8149736
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.658088
Differentiation and Application of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Derived Cardiovascular Cells for Treatment of Heart Diseases: Promises and Challenges
Abstract
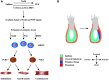
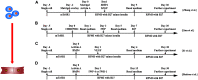
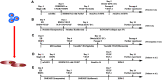
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) are derived from human embryos (human embryonic stem cells) or reprogrammed from human somatic cells (human induced pluripotent stem cells). They can differentiate into cardiovascular cells, which have great potential as exogenous cell resources for restoring cardiac structure and function in patients with heart disease or heart failure. A variety of protocols have been developed to generate and expand cardiovascular cells derived from hPSCs in vitro. Precisely and spatiotemporally activating or inhibiting various pathways in hPSCs is required to obtain cardiovascular lineages with high differentiation efficiency. In this concise review, we summarize the protocols of differentiating hPSCs into cardiovascular cells, highlight their therapeutic application for treatment of cardiac diseases in large animal models, and discuss the challenges and limitations in the use of cardiac cells generated from hPSCs for a better clinical application of hPSC-based cardiac cell therapy.
Keywords: cardiovascular cells; differentiation; human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs); large animal; therapeutic application.
Copyright © 2021 Gao and Pu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Application of human pluripotent stem cells and pluripotent stem cell-derived cellular models for assessing drug toxicity.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2019 Jan;15(1):61-75. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2019.1558207. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30526128 Review.
-
Heart regeneration with human pluripotent stem cells: Prospects and challenges.Bioact Mater. 2020 Jan 14;5(1):74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.01.003. eCollection 2020 Mar. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 31989061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expansion Culture of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells and Production of Cardiomyocytes.Bioengineering (Basel). 2019 May 24;6(2):48. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering6020048. Bioengineering (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31137703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human cardiomyocyte generation from pluripotent stem cells: A state-of-art.Life Sci. 2016 Jan 15;145:98-113. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.12.023. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26682938 Review.
-
Cardiac Regeneration with Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes.Korean Circ J. 2018 Nov;48(11):974-988. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2018.0312. Korean Circ J. 2018. PMID: 30334384 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current genetic models for studying congenital heart diseases: Advantages and disadvantages.Bioinformation. 2024 May 31;20(5):415-429. doi: 10.6026/973206300200415. eCollection 2024. Bioinformation. 2024. PMID: 39132229 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a 3-Dimensional Model to Study Right Heart Dysfunction in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: First Observations.Cells. 2021 Dec 20;10(12):3595. doi: 10.3390/cells10123595. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34944102 Free PMC article.
-
Quality Control of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Colonies by Computational Image Analysis Using Convolutional Neural Networks.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 21;24(1):140. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010140. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613583 Free PMC article.
-
Thermostable Human Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor (TS-bFGF) Engineered with a Disulfide Bond Demonstrates Superior Culture Outcomes in Human Pluripotent Stem Cell.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jun 20;12(6):888. doi: 10.3390/biology12060888. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372172 Free PMC article.
-
A review of protocols for engineering human cardiac organoids.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 7;9(9):e19938. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19938. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809996 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

