Possible Effects of Beetroot Supplementation on Physical Performance Through Metabolic, Neuroendocrine, and Antioxidant Mechanisms: A Narrative Review of the Literature
- PMID: 34055855
- PMCID: PMC8155490
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2021.660150
Possible Effects of Beetroot Supplementation on Physical Performance Through Metabolic, Neuroendocrine, and Antioxidant Mechanisms: A Narrative Review of the Literature
Abstract
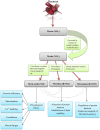
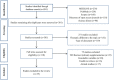
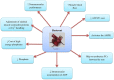
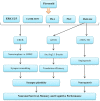
Athletes often seek to use dietary supplements to increase performance during exercise. Among various supplements, much attention has been paid to beetroot in recent years. Beetroot is a source of carbohydrates, fiber, protein, minerals, and vitamins; also, it is a natural source of nitrate and associated with improved sports performance. Nitrates can the modification of skeletal muscle contractile proteins or calcium handling after translation. The time to reach the peak plasma nitrate is between 1 and 3 h after consumption of a single dose of nitrate. Nitrate is metabolized by conversion to nitrite and subsequently nitric oxide. Beetroot can have various effects on athletic performance through nitric oxide. Nitric oxide is an intracellular and extracellular messenger for regulating certain cellular functions and causes vasodilation of blood vessels and increases blood flow. Nitric oxide seems to be effective in improving athletic performance by increasing oxygen, glucose, and other nutrients for better muscle fueling. Nitric oxide plays the main role in anabolic hormones, modulates the release of several neurotransmitters and the major mediators of stress involved in the acute hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal response to exercise. Beetroot is an important source of compounds such as ascorbic acid, carotenoids, phenolic acids, flavonoids, betaline, and highly active phenolics and has high antioxidant properties. Beetroot supplement provides an important source of dietary polyphenols and due to the many health benefits. Phytochemicals of Beetroot through signaling pathways inhibit inflammatory diseases. In this study, the mechanisms responsible for these effects were examined and the research in this regard was reviewed.
Keywords: O2 cost; beetroot supplement; dietary supplements; endurance exercise; nitrate; resistance exercise; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2021 Arazi and Eghbali.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of Nitrate Supplementation on Endurance Cyclic Sports Performance: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2020 Jun 17;12(6):1796. doi: 10.3390/nu12061796. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32560317 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Effects of Beetroot in Athletes and Patients.Cureus. 2019 Dec 11;11(12):e6355. doi: 10.7759/cureus.6355. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31938641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary nitrate supplementation and exercise performance.Sports Med. 2014 May;44 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S35-45. doi: 10.1007/s40279-014-0149-y. Sports Med. 2014. PMID: 24791915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitrate supplementation and human exercise performance: too much of a good thing?Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2015 Nov;18(6):599-604. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000222. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2015. PMID: 26447563 Review.
-
Physicochemical, nutritional, and sensory analyses of a nitrate-enriched beetroot gel and its effects on plasmatic nitric oxide and blood pressure.Food Nutr Res. 2016 Jan 19;60:29909. doi: 10.3402/fnr.v60.29909. eCollection 2016. Food Nutr Res. 2016. PMID: 26790368 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of dietary nitrate supplementation on isometric performance and physiological responses in college bodybuilders: a randomized, double-blind, crossover study.Front Nutr. 2025 May 8;12:1576712. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1576712. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40406159 Free PMC article.
-
Beta vulgaris L. (Beetroot) Methanolic Extract Prevents Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Damage in T2DM Rats by Hypoglycemic, Insulin-Sensitizing, Antioxidant Effects, and Upregulation of PPARα.Biology (Basel). 2021 Dec 9;10(12):1306. doi: 10.3390/biology10121306. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943221 Free PMC article.
-
Red Beetroot's NMR-Based Metabolomics: Phytochemical Profile Related to Development Time and Production Year.Foods. 2021 Aug 15;10(8):1887. doi: 10.3390/foods10081887. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34441664 Free PMC article.
-
Issues on Trainability.Front Physiol. 2022 Jan 24;12:790196. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.790196. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35140629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of acute beetroot juice consumption prior to climbing on lower-body isokinetic and isometric strength, aerobic power, and muscle soreness among mountain climbers.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025 Dec;22(1):2502656. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2025.2502656. Epub 2025 May 5. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40323707 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ormsbee MJ, Lox J, Arciero PJ. Beetroot juice and exercise performance. Nutr Diet Suppl. (2013) 5:27–35. 10.2147/NDS.S52664 - DOI
-
- Baiao D, Silva D, Mere Del Aguila E, Paschoalin V. Nutritional, bioactive and physicochemical characteristics of different beetroot formulations. Food Additives. (2017) 6. 10.5772/intechopen.69301 - DOI
-
- Chawla H, Parle M, Sharma K, Yadav M. Beetroot: a health promoting functional food. Inventi Rapid. (2016) 1: 976–3872.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

