Pooled Analysis of the Accuracy of Xpert Ebola Assay for Diagnosing Ebola Virus Infection
- PMID: 34055977
- PMCID: PMC8147515
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5527505
Pooled Analysis of the Accuracy of Xpert Ebola Assay for Diagnosing Ebola Virus Infection
Abstract
Background: West Africa has witnessed the unprecedented outbreak of Ebola virus disease (EVD). The Ebola virus (EBOV) can cause Ebola hemorrhagic fever, which is documented as the most deadly viral hemorrhagic fever in the world. RT-PCR had been suggested to be employed in the detection of Ebola virus; however, this method has high requirements for laboratory equipment and takes a long time to determine Ebola infection. Although Xpert Ebola is a fast and simple instrument for the detection of Ebola virus, its effect is still unclear. This study is aimed at evaluating the accuracy of Xpert Ebola in diagnosing Ebola virus infection.
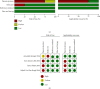
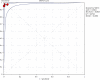
Methods: Using the keywords "Xpert" and "Ebola virus", relevant studies were retrieved from the database of PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane. RT-PCR was employed as a reference standard to evaluate whether the study is eligible to be included in the meta-analysis. Data from these included studies were extracted by two independent assessors and were then analyzed by the Meta-DiSc 1.4 software to produce the heterogeneity of sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SP), positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), and diagnostic advantage ratio (DOR) of the study. The results of pooled analysis were plotted, together with the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve plotted by calculating the area under the curve (AUC). Generated pooled summary estimates (95% CIs) were calculated for the evaluation of the overall accuracy of this study.
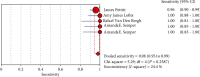
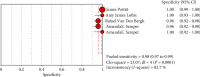
Results: Five fourfold tables were made from the four studies that were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivity of Xpert Ebola was 0.98 (95% confidence interval (CI) (0.95, 0.99)), and the pooled specificity was 0.98 (95% CI (0.97, 0.99)). The pooled values of positive likelihood ratio was 53.91 (95% CI (12.82, 226.79)), with negative likelihood ratio being 0.04 (95% CI (0.02, 0.08)) and diagnostic odds ratio being 2649.45 (95% CI (629.61, 11149.02)). The AUC was 0.9961.
Conclusions: Compared with RT-PCR, Xpert Ebola has high sensitivity and specificity. Therefore, it is a valued alternative method for the clinical diagnosis of Ebola virus infection. However, the Xpert Ebola test is a qualitative test that does not provide quantitative testing of EBOV concentration. Whether it can completely replace other methods or not calls for further evidences.
Copyright © 2021 Zhi-Yong Pan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Performance of the GeneXpert Ebola Assay for Diagnosis of Ebola Virus Disease in Sierra Leone: A Field Evaluation Study.PLoS Med. 2016 Mar 29;13(3):e1001980. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001980. eCollection 2016 Mar. PLoS Med. 2016. PMID: 27023868 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of mycoplasma pneumoniae by loop-mediated isothermal amplification: systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Feb 19;19(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-3799-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30782134 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Diagnostic Efficacy of Xpert CT/NG for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 8;2020:2892734. doi: 10.1155/2020/2892734. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33102576 Free PMC article.
-
Development, Evaluation, and Integration of a Quantitative Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction Diagnostic Test for Ebola Virus on a Molecular Diagnostics Platform.J Infect Dis. 2016 Oct 15;214(suppl 3):S192-S202. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw150. Epub 2016 May 30. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27247341 Free PMC article.
-
Xpert MTB/RIF Assay for the Diagnosis of Lymph Node Tuberculosis in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2022 Aug 8;11(15):4616. doi: 10.3390/jcm11154616. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35956230 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of Xpert® Mpox and STANDARD™ M10 MPX/OPX for the detection of monkeypox virus.J Infect. 2025 Feb;90(2):106413. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2025.106413. Epub 2025 Jan 15. J Infect. 2025. PMID: 39824291 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical