Covid-19 Pneumonia and Ventilation-induced Lung Injury: A Case Report
- PMID: 34056135
- PMCID: PMC8158325
- DOI: 10.2478/rjaic-2020-0020
Covid-19 Pneumonia and Ventilation-induced Lung Injury: A Case Report
Abstract
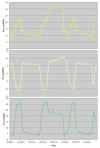
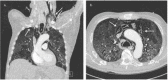
We present the case of a 67-year-old male patient, who was admitted to the intensive care unit for hypoxemic respiratory failure due to severe COVID-19 pneumonitis, requiring mechanical ventilation. Despite close monitoring using transpulmonary pressure measurements and interventions to pursue lung-protective ventilation, the patient developed extensive barotrauma including a right-sided pneumothorax, subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum while on pressure support ventilation. We hypothesize that the high respiratory drive that COVID-19 patients seem to exhibit, combined with diffuse alveolar injury and increased alveolar pressure, resulted in gross barotrauma.
Conclusion: The respiratory characteristics that COVID-19 patients seem to exhibit might expose those on mechanical ventilation to an increased risk of developing ventilation-induced lung injury. This case emphasizes that caution should be taken in the respiratory treatment of patients with COVID-19 pneumonitis.
Keywords: COVID-19 pneumonia; ICU; barotrauma; mechanical ventilation; pneumomediastinum.
© 2020 Lieke H.A. van Gastel, MD et al. published by Sciendo.
Figures
References
-
- Brochard L, Slutsky A, Pesenti A. Mechanical Ventilation to Minimize Progression of Lung Injury in Acute Respiratory Failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195(4):438–442. Feb 15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
