Intramuscular Electrical Stimulation Combined with Therapeutic Exercises in Patients with Shoulder Adhesive Capsulitis: A Randomised Controlled Trial
- PMID: 34056148
- PMCID: PMC8139297
- DOI: 10.29337/ijsp.25
Intramuscular Electrical Stimulation Combined with Therapeutic Exercises in Patients with Shoulder Adhesive Capsulitis: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Myofascial trigger points (MTrPs) precipitate the shoulder pain severity and disability in patients with shoulder adhesive capsulitis (SAC). This study aims to compare the effectiveness of intramuscular electrical stimulation (IMES) combined with therapeutic exercises versus dry needling (DN) combined with therapeutic exercises in improving the clinical outcomes in patients with SAC.
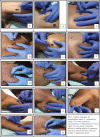
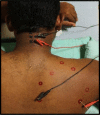
Methods and materials: In this randomized controlled trial, IMES (n = 45) and DN (43) groups had received respectively IMES, and DN twice weekly for three consecutive weeks. Both groups received therapeutic exercises 1520 minutes, five days in a week during the second and third week. Pain, disability, kinesiophobia, number of active and latent MTrPs, shoulder abduction and external rotation range of motion were assessed at baseline, week-1, week-2, week-3 and follow-up at 3 months. A repeated measures ANOVA performed to find out the significant differences in the clinical outcomes between the groups.
Results: The results of repeated measures of ANOVA shows that the post intervention timelines assessment scores of VAS, DASH, shoulder abduction and external rotation ROM, number of active and latent MTrPs and kinesiophobia were significantly (p. < 0.05) improved in both groups. However, IMES group had achieved a greater improvement over DN group (p. < 0.05) on the shoulder pain severity and disability, shoulder range of motion, number of active and latent MTrPs and kinesiophobia. Despite the significant statistical differences between the groups, IMES group did not achieve the minimal clinically important differences of 1.5cm and 11-points respectively for the VAS and DASH scores. No serious adverse effects occurred during the three weeks of treatment.
Conclusion: IMES combined with therapeutic exercises is an effective treatment to reduce the shoulder pain severity and upper limb disability by deactivating the active and latent MTrPs and improving the shoulder abduction and external rotation range of motion in patients with SAC.
Keywords: Dry needling; Electrical stimulation; Myofascial pain; Shoulder exercises; Trigger points; adhesive capsulitis; frozen shoulder; shoulder pain.
Copyright: 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Short-term effect of myofascial trigger point dry-needling in patients with Adhesive Capsulitis.J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2021 Jan;25:146-150. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2020.10.014. Epub 2020 Oct 26. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2021. PMID: 33714486
-
Rate and maintenance of improvement of myofascial pain with dry needling alone vs. dry needling with intramuscular electrical stimulation: a randomized controlled trial.J Man Manip Ther. 2021 Aug;29(4):216-226. doi: 10.1080/10669817.2020.1824469. Epub 2020 Sep 29. J Man Manip Ther. 2021. PMID: 32990529 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of a static progressive stretch device as an adjunct to physical therapy in treating adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: a prospective, randomised study.Physiotherapy. 2014 Sep;100(3):228-34. doi: 10.1016/j.physio.2013.08.006. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Physiotherapy. 2014. PMID: 24211154 Clinical Trial.
-
The prevalence of myofascial trigger points in neck and shoulder-related disorders: a systematic review of the literature.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018 Jul 25;19(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s12891-018-2157-9. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018. PMID: 30045708 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Dry Needling of Myofascial Trigger Points in the Triceps Surae Muscles: Systematic Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Sep 24;10(10):1862. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10101862. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of intramuscular electrical stimulation using conventional and inverse electrode placement methods on pressure pain threshold and electromyographic activity of the upper trapezius muscle with myofascial trigger points: a randomized clinical trial.Korean J Pain. 2025 Apr 1;38(2):187-197. doi: 10.3344/kjp.24332. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Korean J Pain. 2025. PMID: 40108770 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis and Non-Surgical Treatment of Primary Frozen Shoulder.Ann Rehabil Med. 2025 Jun;49(3):113-138. doi: 10.5535/arm.250057. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Ann Rehabil Med. 2025. PMID: 40602400 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Dry Needling With Electrical Stimulation on Pain and Disability in Patients With Musculoskeletal Shoulder Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Cureus. 2023 Jul 5;15(7):e41404. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41404. eCollection 2023 Jul. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37546088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

